This is the tiny developer documentation for Hono.
# Start of Hono documentation
# Hono
Hono - 在日语中是火焰🔥的意思 - 是一个基于 Web 标准构建的小型、简单且超快的 Web 框架。它适用于任何 JavaScript 运行时:Cloudflare Workers、Fastly Compute、Deno、Bun、Vercel、Netlify、AWS Lambda、Lambda@Edge 和 Node.js。
¥Hono - ***means flame🔥 in Japanese*** - is a small, simple, and ultrafast web framework built on Web Standards.
It works on any JavaScript runtime: Cloudflare Workers, Fastly Compute, Deno, Bun, Vercel, Netlify, AWS Lambda, Lambda@Edge, and Node.js.
快速,但不仅仅是快速。
¥Fast, but not only fast.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hono!'))
export default app
```
## 快速入门
¥Quick Start
只需运行这个:
¥Just run this:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono@latest
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono@latest
```
:::
## 功能
¥Features
* 超快 🚀 - 路由 `RegExpRouter` 非常快。不使用线性循环。快速。
¥**Ultrafast** 🚀 - The router `RegExpRouter` is really fast. Not using linear loops. Fast.
* 轻量级 🪶 - `hono/tiny` 预设小于 14kB。Hono 没有任何依赖,仅使用 Web 标准。
¥**Lightweight** 🪶 - The `hono/tiny` preset is under 14kB. Hono has zero dependencies and uses only the Web Standards.
* 多运行时 🌍 - 适用于 Cloudflare Workers、Fastly Compute、Deno、Bun、AWS Lambda 或 Node.js。相同的代码在所有平台上运行。
¥**Multi-runtime** 🌍 - Works on Cloudflare Workers, Fastly Compute, Deno, Bun, AWS Lambda, or Node.js. The same code runs on all platforms.
* 包含适配 🔋 - Hono 具有内置中间件、自定义中间件、第三方中间件和助手。包含适配。
¥**Batteries Included** 🔋 - Hono has built-in middleware, custom middleware, third-party middleware, and helpers. Batteries included.
* Delightful DX 😃 - 超级干净的 API。一流的 TypeScript 支持。现在,我们得到了 "类型"。
¥**Delightful DX** 😃 - Super clean APIs. First-class TypeScript support. Now, we've got "Types".
## 用例
¥Use-cases
Hono 是一个类似于 Express 的简单 Web 应用框架,没有前端。但它在 CDN Edges 上运行,并允许你与中间件结合使用时构建更大的应用。以下是一些用例示例。
¥Hono is a simple web application framework similar to Express, without a frontend.
But it runs on CDN Edges and allows you to construct larger applications when combined with middleware.
Here are some examples of use-cases.
* 构建 Web API
¥Building Web APIs
* 后端服务器的代理
¥Proxy of backend servers
* CDN 前端
¥Front of CDN
* Edge 应用
¥Edge application
* 库的基本服务器
¥Base server for a library
* 全栈应用
¥Full-stack application
## 谁在使用 Hono?
¥Who is using Hono?
| 项目 | 平台 | 用于什么? |
| ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com) | Cloudflare Workers | 免费开源 CDN 服务。Hono 用于 API 服务器。 |
| [Cloudflare D1](https://www.cloudflare.com/developer-platform/d1/) | Cloudflare Workers | 无服务器 SQL 数据库。Hono 用于内部 API 服务器。 |
| [Cloudflare Workers KV](https://www.cloudflare.com/developer-platform/workers-kv/) | Cloudflare Workers | 无服务器键值数据库。Hono 用于内部 API 服务器。 |
| [BaseAI](https://baseai.dev) | 本地 AI 服务器 | 带内存的无服务器 AI 代理管道。一个用于 Web 的开源代理 AI 框架。带有 Hono 的 API 服务器。 |
| [Unkey](https://unkey.dev) | Cloudflare Workers | 一个开源 API 身份验证和授权。Hono 用于 API 服务器。 |
| [OpenStatus](https://openstatus.dev) | Bun | 一个开源网站和 API 监控平台。Hono 用于 API 服务器。 |
| [Deno 基准测试](https://deno.com/benchmarks) | Deno | 基于 V8 构建的安全 TypeScript 运行时。Hono 用于基准测试。 |
以及以下内容。
¥And the following.
* [Drivly](https://driv.ly/) - Cloudflare Workers
* [repeat.dev](https://repeat.dev/) - Cloudflare Workers
你想看更多吗?参见 [谁在生产中使用 Hono?](https://github.com/orgs/honojs/discussions/1510)。
¥Do you want to see more? See [Who is using Hono in production?](https://github.com/orgs/honojs/discussions/1510).
## 1 分钟内掌握 Hono
¥Hono in 1 minute
使用 Hono 为 Cloudflare Workers 创建应用的演示。
¥A demonstration to create an application for Cloudflare Workers with Hono.

## 超快
¥Ultrafast
与 Cloudflare Workers 的其他路由相比,Hono 是最快的。
¥**Hono is the fastest**, compared to other routers for Cloudflare Workers.
```
Hono x 402,820 ops/sec ±4.78% (80 runs sampled)
itty-router x 212,598 ops/sec ±3.11% (87 runs sampled)
sunder x 297,036 ops/sec ±4.76% (77 runs sampled)
worktop x 197,345 ops/sec ±2.40% (88 runs sampled)
Fastest is Hono
✨ Done in 28.06s.
```
参见 [更多基准](/docs/concepts/benchmarks)。
¥See [more benchmarks](/docs/concepts/benchmarks).
## 轻量级
¥Lightweight
Hono 很小。使用 `hono/tiny` 预设,其大小在最小化时低于 14KB。有许多中间件和适配器,但它们仅在使用时打包在一起。有关上下文,Express 的大小为 572KB。
¥**Hono is so small**. With the `hono/tiny` preset, its size is **under 14KB** when minified. There are many middleware and adapters, but they are bundled only when used. For context, the size of Express is 572KB.
```
$ npx wrangler dev --minify ./src/index.ts
⛅️ wrangler 2.20.0
--------------------
⬣ Listening at http://0.0.0.0:8787
- http://127.0.0.1:8787
- http://192.168.128.165:8787
Total Upload: 11.47 KiB / gzip: 4.34 KiB
```
## 多个路由
¥Multiple routers
Hono 有多个路由。
¥**Hono has multiple routers**.
RegExpRouter 是 JavaScript 世界中最快的路由。它使用在调度之前创建的单个大型正则表达式来匹配路由。使用 SmartRouter,它支持所有路由模式。
¥**RegExpRouter** is the fastest router in the JavaScript world. It matches the route using a single large Regex created before dispatch. With **SmartRouter**, it supports all route patterns.
LinearRouter 可以非常快速地注册路由,因此它适用于每次初始化应用的环境。PatternRouter 只是添加和匹配模式,使其变小。
¥**LinearRouter** registers the routes very quickly, so it's suitable for an environment that initializes applications every time. **PatternRouter** simply adds and matches the pattern, making it small.
参见 [有关路由的更多信息](/docs/concepts/routers)。
¥See [more information about routes](/docs/concepts/routers).
## Web 标准
¥Web Standards
由于使用了 Web 标准,Hono 可以在很多平台上运行。
¥Thanks to the use of the **Web Standards**, Hono works on a lot of platforms.
* Cloudflare Workers
* Cloudflare 页面
¥Cloudflare Pages
* Fastly 计算
¥Fastly Compute
* Deno
* Bun
* Vercel
* AWS Lambda
* Lambda@Edge
* 其他
¥Others
通过使用 [Node.js 适配器](https://github.com/honojs/node-server),Hono 可以在 Node.js 上运行。
¥And by using [a Node.js adapter](https://github.com/honojs/node-server), Hono works on Node.js.
参见 [有关 Web 标准的更多信息](/docs/concepts/web-standard)。
¥See [more information about Web Standards](/docs/concepts/web-standard).
## 中间件和助手
¥Middleware & Helpers
Hono 有许多中间件和助手。这使 "写得少,做得多" 成为现实。
¥**Hono has many middleware and helpers**. This makes "Write Less, do more" a reality.
开箱即用,Hono 提供中间件和助手:
¥Out of the box, Hono provides middleware and helpers for:
* [基本身份验证](/docs/middleware/builtin/basic-auth)
¥[Basic Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/basic-auth)
* [承载身份验证](/docs/middleware/builtin/bearer-auth)
¥[Bearer Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/bearer-auth)
* [主体限制](/docs/middleware/builtin/body-limit)
¥[Body Limit](/docs/middleware/builtin/body-limit)
* [缓存](/docs/middleware/builtin/cache)
¥[Cache](/docs/middleware/builtin/cache)
* [压缩](/docs/middleware/builtin/compress)
¥[Compress](/docs/middleware/builtin/compress)
* [上下文存储](/docs/middleware/builtin/context-storage)
¥[Context Storage](/docs/middleware/builtin/context-storage)
* [Cookie](/docs/helpers/cookie)
* [CORS](/docs/middleware/builtin/cors)
* [ETag](/docs/middleware/builtin/etag)
* [html](/docs/helpers/html)
* [JSX](/docs/guides/jsx)
* [JWT 身份验证](/docs/middleware/builtin/jwt)
¥[JWT Authentication](/docs/middleware/builtin/jwt)
* [日志器](/docs/middleware/builtin/logger)
¥[Logger](/docs/middleware/builtin/logger)
* [语言](/docs/middleware/builtin/language)
¥[Language](/docs/middleware/builtin/language)
* [漂亮的 JSON](/docs/middleware/builtin/pretty-json)
¥[Pretty JSON](/docs/middleware/builtin/pretty-json)
* [安全标头](/docs/middleware/builtin/secure-headers)
¥[Secure Headers](/docs/middleware/builtin/secure-headers)
* [SSG](/docs/helpers/ssg)
* [流式传输](/docs/helpers/streaming)
¥[Streaming](/docs/helpers/streaming)
* [GraphQL 服务器](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/graphql-server)
¥[GraphQL Server](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/graphql-server)
* [Firebase 身份验证](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/firebase-auth)
¥[Firebase Authentication](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/firebase-auth)
* [Sentry](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/sentry)
* 其他!
¥Others!
例如,使用 Hono 添加 ETag 和请求日志记录只需要几行代码:
¥For example, adding ETag and request logging only takes a few lines of code with Hono:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { etag } from 'hono/etag'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
const app = new Hono()
app.use(etag(), logger())
```
参见 [有关中间件的更多信息](/docs/concepts/middleware)。
¥See [more information about Middleware](/docs/concepts/middleware).
## 开发者体验
¥Developer Experience
Hono 提供了令人愉悦的 "开发者体验"。
¥Hono provides a delightful "**Developer Experience**".
借助 `Context` 对象,可以轻松访问请求/响应。此外,Hono 是用 TypeScript 编写的。Hono 有 "类型"。
¥Easy access to Request/Response thanks to the `Context` object.
Moreover, Hono is written in TypeScript. Hono has "**Types**".
例如,路径参数将是字面量类型。
¥For example, the path parameters will be literal types.
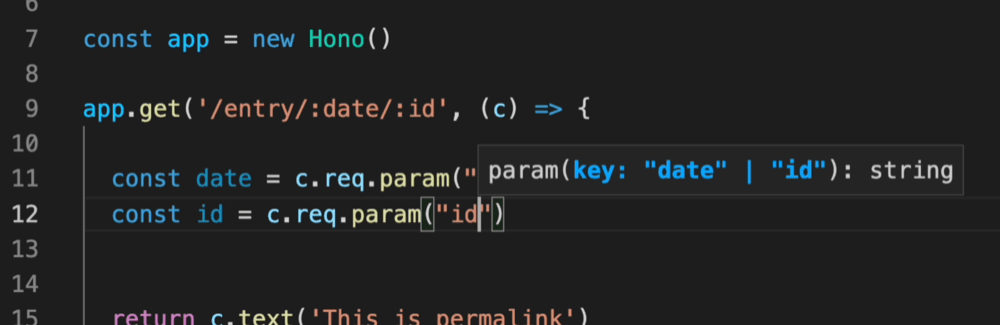
Validator 和 Hono Client `hc` 启用了 RPC 模式。在 RPC 模式下,你可以使用自己喜欢的验证器(例如 Zod),并轻松地与客户端共享服务器端 API 规范并构建类型安全的应用。
¥And, the Validator and Hono Client `hc` enable the RPC mode. In RPC mode,
you can use your favorite validator such as Zod and easily share server-side API specs with the client and build type-safe applications.
参见 [Hono Stacks](/docs/concepts/stacks)。
¥See [Hono Stacks](/docs/concepts/stacks).
# 最佳实践
¥Best Practices
Hono 非常灵活。你可以根据需要编写应用。但是,有更好的最佳实践可以遵循。
¥Hono is very flexible. You can write your app as you like.
However, there are best practices that are better to follow.
## 尽可能不要制作 "控制器"
¥Don't make "Controllers" when possible
如果可能,你不应创建 "类似 Ruby on Rails 的控制器"。
¥When possible, you should not create "Ruby on Rails-like Controllers".
```ts
// 🙁
// A RoR-like Controller
const booksList = (c: Context) => {
return c.json('list books')
}
app.get('/books', booksList)
```
问题与类型有关。例如,如果不编写复杂的泛型,则无法在 Controller 中推断路径参数。
¥The issue is related to types. For example, the path parameter cannot be inferred in the Controller without writing complex generics.
```ts
// 🙁
// A RoR-like Controller
const bookPermalink = (c: Context) => {
const id = c.req.param('id') // Can't infer the path param
return c.json(`get ${id}`)
}
```
因此,你不需要创建类似 RoR 的控制器,而应该在路径定义后直接编写处理程序。
¥Therefore, you don't need to create RoR-like controllers and should write handlers directly after path definitions.
```ts
// 😃
app.get('/books/:id', (c) => {
const id = c.req.param('id') // Can infer the path param
return c.json(`get ${id}`)
})
```
## `hono/factory` 中的 `factory.createHandlers()`
¥`factory.createHandlers()` in `hono/factory`
如果你仍想创建类似 RoR 的控制器,请在 [`hono/factory`](/docs/helpers/factory) 中使用 `factory.createHandlers()`。如果你使用这种方法,类型推断将正常工作。
¥If you still want to create a RoR-like Controller, use `factory.createHandlers()` in [`hono/factory`](/docs/helpers/factory). If you use this, type inference will work correctly.
```ts
import { createFactory } from 'hono/factory'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
// ...
// 😃
const factory = createFactory()
const middleware = factory.createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
c.set('foo', 'bar')
await next()
})
const handlers = factory.createHandlers(logger(), middleware, (c) => {
return c.json(c.var.foo)
})
app.get('/api', ...handlers)
```
## 构建更大的应用
¥Building a larger application
使用 `app.route()` 构建更大的应用而无需创建 "类似 Ruby on Rails 的控制器"。
¥Use `app.route()` to build a larger application without creating "Ruby on Rails-like Controllers".
如果你的应用有 `/authors` 和 `/books` 端点,并且你希望将文件与 `index.ts` 分开,请创建 `authors.ts` 和 `books.ts`。
¥If your application has `/authors` and `/books` endpoints and you wish to separate files from `index.ts`, create `authors.ts` and `books.ts`.
```ts
// authors.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.json('list authors'))
app.post('/', (c) => c.json('create an author', 201))
app.get('/:id', (c) => c.json(`get ${c.req.param('id')}`))
export default app
```
```ts
// books.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.json('list books'))
app.post('/', (c) => c.json('create a book', 201))
app.get('/:id', (c) => c.json(`get ${c.req.param('id')}`))
export default app
```
然后,导入它们并将其与 `app.route()` 一起挂载在路径 `/authors` 和 `/books` 上。
¥Then, import them and mount on the paths `/authors` and `/books` with `app.route()`.
```ts
// index.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import authors from './authors'
import books from './books'
const app = new Hono()
// 😃
app.route('/authors', authors)
app.route('/books', books)
export default app
```
### 如果要使用 RPC 功能
¥If you want to use RPC features
上面的代码对于正常用例来说效果很好。但是,如果你想使用 `RPC` 功能,可以通过如下链接获取正确的类型。
¥The code above works well for normal use cases.
However, if you want to use the `RPC` feature, you can get the correct type by chaining as follows.
```ts
// authors.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
.get('/', (c) => c.json('list authors'))
.post('/', (c) => c.json('create an author', 201))
.get('/:id', (c) => c.json(`get ${c.req.param('id')}`))
export default app
```
如果你将 `app` 的类型传递给 `hc`,它将获得正确的类型。
¥If you pass the type of the `app` to `hc`, it will get the correct type.
```ts
import app from './authors'
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
// 😃
const client = hc('http://localhost') // Typed correctly
```
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 [RPC 页面](/docs/guides/rpc#using-rpc-with-larger-applications)。
¥For more detailed information, please see [the RPC page](/docs/guides/rpc#using-rpc-with-larger-applications).
# 示例
¥Examples
查看 [示例部分](/examples/)。
¥See the [Examples section](/examples/).
# 常见问题
¥Frequently Asked Questions
本指南收集了有关 Hono 的常见问题 (FAQ) 及其解决方法。
¥This guide is a collection of frequently asked questions (FAQ) about Hono and how to resolve them.
## Hono 有官方的 Renovate 配置吗?
¥Is there an official Renovate config for Hono?
Hono 团队目前不维护 [Renovate](https://github.com/renovatebot/renovate) 配置。因此,请按如下方式使用第三方 renovate-config。
¥The Hono teams does not currently maintain [Renovate](https://github.com/renovatebot/renovate) Configuration.
Therefore, please use third-party renovate-config as follows.
在你的 `renovate.json` 中:
¥In your `renovate.json` :
```json
// renovate.json
{
"$schema": "https://docs.renovatebot.com/renovate-schema.json",
"extends": [
"github>shinGangan/renovate-config-hono" // [!code ++]
]
}
```
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 [renovate-config-hono](https://github.com/shinGangan/renovate-config-hono) 存储库。
¥see [renovate-config-hono](https://github.com/shinGangan/renovate-config-hono) repository for more details.
# 助手工具
¥Helpers
辅助程序可用于协助开发你的应用。与中间件不同,它们不充当处理程序,而是提供有用的功能。
¥Helpers are available to assist in developing your application. Unlike middleware, they don't act as handlers, but rather provide useful functions.
例如,以下是如何使用 [Cookie 助手](/docs/helpers/cookie):
¥For instance, here's how to use the [Cookie helper](/docs/helpers/cookie):
```ts
import { getCookie, setCookie } from 'hono/cookie'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/cookie', (c) => {
const yummyCookie = getCookie(c, 'yummy_cookie')
// ...
setCookie(c, 'delicious_cookie', 'macha')
//
})
```
## 可用助手
¥Available Helpers
* [接受](/docs/helpers/accepts)
¥[Accepts](/docs/helpers/accepts)
* [适配器](/docs/helpers/adapter)
¥[Adapter](/docs/helpers/adapter)
* [Cookie](/docs/helpers/cookie)
* [css](/docs/helpers/css)
* [开发](/docs/helpers/dev)
¥[Dev](/docs/helpers/dev)
* [工厂](/docs/helpers/factory)
¥[Factory](/docs/helpers/factory)
* [html](/docs/helpers/html)
* [JWT](/docs/helpers/jwt)
* [SSG](/docs/helpers/ssg)
* [流式传输](/docs/helpers/streaming)
¥[Streaming](/docs/helpers/streaming)
* [测试](/docs/helpers/testing)
¥[Testing](/docs/helpers/testing)
* [WebSocket](/docs/helpers/websocket)
# 客户端组件
¥Client Components
`hono/jsx` 不仅支持服务器端,还支持客户端。这意味着可以创建一个在浏览器中运行的交互式 UI。我们称之为客户端组件或 `hono/jsx/dom`。
¥`hono/jsx` supports not only server side but also client side. This means that it is possible to create an interactive UI that runs in the browser. We call it Client Components or `hono/jsx/dom`.
它速度快而且非常小。`hono/jsx/dom` 中的计数器程序使用 Brotli 压缩后只有 2.8KB。但是,React 占用 47.8KB。
¥It is fast and very small. The counter program in `hono/jsx/dom` is only 2.8KB with Brotli compression. But, 47.8KB for React.
本节介绍客户端组件特有的功能。
¥This section introduces Client Components-specific features.
## 反例
¥Counter example
以下是简单计数器的示例,相同的代码与 React 中的工作方式相同。
¥Here is an example of a simple counter, the same code works as in React.
```tsx
import { useState } from 'hono/jsx'
import { render } from 'hono/jsx/dom'
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
return (
Count: {count}
)
}
function App() {
return (
)
}
const root = document.getElementById('root')
render(, root)
```
## `render()`
你可以使用 `render()` 在指定的 HTML 元素内插入 JSX 组件。
¥You can use `render()` to insert JSX components within a specified HTML element.
```tsx
render(, container)
```
## 与 React 兼容的 Hooks
¥Hooks compatible with React
hono/jsx/dom 具有与 React 兼容或部分兼容的 Hooks。你可以通过查看 [React 文档](https://react.nodejs.cn/reference/react/hooks) 来了解这些 API。
¥hono/jsx/dom has Hooks that are compatible or partially compatible with React. You can learn about these APIs by looking at [the React documentation](https://react.nodejs.cn/reference/react/hooks).
* `useState()`
* `useEffect()`
* `useRef()`
* `useCallback()`
* `use()`
* `startTransition()`
* `useTransition()`
* `useDeferredValue()`
* `useMemo()`
* `useLayoutEffect()`
* `useReducer()`
* `useDebugValue()`
* `createElement()`
* `memo()`
* `isValidElement()`
* `useId()`
* `createRef()`
* `forwardRef()`
* `useImperativeHandle()`
* `useSyncExternalStore()`
* `useInsertionEffect()`
* `useFormStatus()`
* `useActionState()`
* `useOptimistic()`
## `startViewTransition()` 系列
¥`startViewTransition()` family
`startViewTransition()` 系列包含原始钩子和函数,可轻松处理 [查看转换 API](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/View_Transitions_API)。以下是如何使用它们的示例。
¥The `startViewTransition()` family contains original hooks and functions to handle [View Transitions API](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/View_Transitions_API) easily. The followings are examples of how to use them.
### 1. 最简单的例子
¥ An easiest example
你可以使用 `document.startViewTransition` 或 `startViewTransition()` 语法编写过渡。
¥You can write a transition using the `document.startViewTransition` shortly with the `startViewTransition()`.
```tsx
import { useState, startViewTransition } from 'hono/jsx'
import { css, Style } from 'hono/css'
export default function App() {
const [showLargeImage, setShowLargeImage] = useState(false)
return (
<>
{!showLargeImage ? (
) : (
)}
)
}
```
### 2. 将 `viewTransition()` 与 `keyframes()` 一起使用
¥ Using `viewTransition()` with `keyframes()`
`viewTransition()` 函数允许你获取唯一的 `view-transition-name`。
¥The `viewTransition()` function allows you to get the unique `view-transition-name`.
你可以将它与 `keyframes()` 一起使用,`::view-transition-old()` 转换为 `::view-transition-old(${uniqueName))`。
¥You can use it with the `keyframes()`, The `::view-transition-old()` is converted to `::view-transition-old(${uniqueName))`.
```tsx
import { useState, startViewTransition } from 'hono/jsx'
import { viewTransition } from 'hono/jsx/dom/css'
import { css, keyframes, Style } from 'hono/css'
const rotate = keyframes`
from {
rotate: 0deg;
}
to {
rotate: 360deg;
}
`
export default function App() {
const [showLargeImage, setShowLargeImage] = useState(false)
const [transitionNameClass] = useState(() =>
viewTransition(css`
::view-transition-old() {
animation-name: ${rotate};
}
::view-transition-new() {
animation-name: ${rotate};
}
`)
)
return (
<>
{!showLargeImage ? (
) : (
)}
)
}
```
### 3. 使用 `useViewTransition`
¥ Using `useViewTransition`
如果只想在动画期间更改样式。你可以使用 `useViewTransition()`。此钩子返回 `[boolean, (callback: () => void) => void]`,它们是 `isUpdating` 标志和 `startViewTransition()` 函数。
¥If you want to change the style only during the animation. You can use `useViewTransition()`. This hook returns the `[boolean, (callback: () => void) => void]`, and they are the `isUpdating` flag and the `startViewTransition()` function.
使用此钩子时,组件将在以下两次进行评估。
¥When this hook is used, the Component is evaluated at the following two times.
* 在对 `startViewTransition()` 的调用的回调中。
¥Inside the callback of a call to `startViewTransition()`.
* 当 [`finish` promise 实现](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/ViewTransition/finished) 时
¥When [the `finish` promise becomes fulfilled](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/ViewTransition/finished)
```tsx
import { useState, useViewTransition } from 'hono/jsx'
import { viewTransition } from 'hono/jsx/dom/css'
import { css, keyframes, Style } from 'hono/css'
const rotate = keyframes`
from {
rotate: 0deg;
}
to {
rotate: 360deg;
}
`
export default function App() {
const [isUpdating, startViewTransition] = useViewTransition()
const [showLargeImage, setShowLargeImage] = useState(false)
const [transitionNameClass] = useState(() =>
viewTransition(css`
::view-transition-old() {
animation-name: ${rotate};
}
::view-transition-new() {
animation-name: ${rotate};
}
`)
)
return (
<>
{!showLargeImage ? (
) : (
)}
)
}
```
## `hono/jsx/dom` 运行时
¥The `hono/jsx/dom` runtime
有一个用于客户端组件的小型 JSX 运行时。使用它将产生比使用 `hono/jsx` 更小的打包结果。在 `tsconfig.json` 中指定 `hono/jsx/dom`。对于 Deno,修改 deno.json。
¥There is a small JSX Runtime for Client Components. Using this will result in smaller bundled results than using `hono/jsx`. Specify `hono/jsx/dom` in `tsconfig.json`. For Deno, modify the deno.json.
```json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"jsx": "react-jsx",
"jsxImportSource": "hono/jsx/dom"
}
}
```
# JSX
你可以使用 `hono/jsx` 和 JSX 语法编写 HTML。
¥You can write HTML with JSX syntax with `hono/jsx`.
虽然 `hono/jsx` 在客户端上运行,但你可能最常在服务器端渲染内容时使用它。以下是与 JSX 相关的一些内容,这些内容对服务器和客户端都很常见。
¥Although `hono/jsx` works on the client, you will probably use it most often when rendering content on the server side. Here are some things related to JSX that are common to both server and client.
## 设置
¥Settings
要使用 JSX,请修改 `tsconfig.json`:
¥To use JSX, modify the `tsconfig.json`:
`tsconfig.json`:
```json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"jsx": "react-jsx",
"jsxImportSource": "hono/jsx"
}
}
```
或者,使用 pragma 指令:
¥Alternatively, use the pragma directives:
```ts
/** @jsx jsx */
/** @jsxImportSource hono/jsx */
```
对于 Deno,你必须修改 `deno.json` 而不是 `tsconfig.json`:
¥For Deno, you have to modify the `deno.json` instead of the `tsconfig.json`:
```json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"jsx": "precompile",
"jsxImportSource": "hono/jsx"
}
}
```
## 用法
¥Usage
`index.tsx`:
```tsx
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import type { FC } from 'hono/jsx'
const app = new Hono()
const Layout: FC = (props) => {
return (
{props.children}
)
}
const Top: FC<{ messages: string[] }> = (props: {
messages: string[]
}) => {
return (
Hello Hono!
{props.messages.map((message) => {
return
{message}!!
})}
)
}
app.get('/', (c) => {
const messages = ['Good Morning', 'Good Evening', 'Good Night']
return c.html()
})
export default app
```
## 片段
¥Fragment
使用 Fragment 对多个元素进行分组,而无需添加额外的节点:
¥Use Fragment to group multiple elements without adding extra nodes:
```tsx
import { Fragment } from 'hono/jsx'
const List = () => (
first child
second child
third child
)
```
或者,如果设置正确,你可以使用 `<>` 编写它。
¥Or you can write it with `<>` if it set up properly.
```tsx
const List = () => (
<>
first child
second child
third child
)
```
## `PropsWithChildren`
你可以使用 `PropsWithChildren` 正确地推断函数组件中的子元素。
¥You can use `PropsWithChildren` to correctly infer a child element in a function component.
```tsx
import { PropsWithChildren } from 'hono/jsx'
type Post = {
id: number
title: string
}
function Component({ title, children }: PropsWithChildren) {
return (
{title}
{children}
)
}
```
## 插入原始 HTML
¥Inserting Raw HTML
要直接插入 HTML,请使用 `dangerouslySetInnerHTML`:
¥To directly insert HTML, use `dangerouslySetInnerHTML`:
```tsx
app.get('/foo', (c) => {
const inner = { __html: 'JSX · SSR' }
const Div =
})
```
## 记忆化
¥Memoization
通过使用 `memo` 记忆计算字符串来优化你的组件:
¥Optimize your components by memoizing computed strings using `memo`:
```tsx
import { memo } from 'hono/jsx'
const Header = memo(() => Welcome to Hono)
const Footer = memo(() => )
const Layout = (
Hono is cool!
)
```
## 上下文
¥Context
通过使用 `useContext`,你可以在组件树的任何级别上全局共享数据,而无需通过 props 传递值。
¥By using `useContext`, you can share data globally across any level of the Component tree without passing values through props.
```tsx
import type { FC } from 'hono/jsx'
import { createContext, useContext } from 'hono/jsx'
const themes = {
light: {
color: '#000000',
background: '#eeeeee',
},
dark: {
color: '#ffffff',
background: '#222222',
},
}
const ThemeContext = createContext(themes.light)
const Button: FC = () => {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext)
return
}
const Toolbar: FC = () => {
return (
)
}
// ...
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
)
})
```
## 异步组件
¥Async Component
`hono/jsx` 支持异步组件,因此你可以在组件中使用 `async`/`await`。如果你使用 `c.html()` 渲染它,它将自动等待。
¥`hono/jsx` supports an Async Component, so you can use `async`/`await` in your component.
If you render it with `c.html()`, it will await automatically.
```tsx
const AsyncComponent = async () => {
await new Promise((r) => setTimeout(r, 1000)) // sleep 1s
return
Done!
}
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
)
})
```
## Suspense
¥Suspense
类似 React 的 `Suspense` 功能可用。如果你用 `Suspense` 封装异步组件,则 fallback 中的内容将首先渲染,一旦 Promise 被解析,将显示等待的内容。你可以将它与 `renderToReadableStream()` 一起使用。
¥The React-like `Suspense` feature is available.
If you wrap the async component with `Suspense`, the content in the fallback will be rendered first, and once the Promise is resolved, the awaited content will be displayed.
You can use it with `renderToReadableStream()`.
```tsx
import { renderToReadableStream, Suspense } from 'hono/jsx/streaming'
//...
app.get('/', (c) => {
const stream = renderToReadableStream(
loading...}>
)
return c.body(stream, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=UTF-8',
'Transfer-Encoding': 'chunked',
},
})
})
```
## ErrorBoundary
¥ErrorBoundary
你可以使用 `ErrorBoundary` 捕获子组件中的错误。
¥You can catch errors in child components using `ErrorBoundary`.
在下面的示例中,如果发生错误,它将显示 `fallback` 中指定的内容。
¥In the example below, it will show the content specified in `fallback` if an error occurs.
```tsx
function SyncComponent() {
throw new Error('Error')
return
Hello
}
app.get('/sync', async (c) => {
return c.html(
Out of Service}>
)
})
```
`ErrorBoundary` 还可以与异步组件和 `Suspense` 一起使用。
¥`ErrorBoundary` can also be used with async components and `Suspense`.
```tsx
async function AsyncComponent() {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 2000))
throw new Error('Error')
return
Hello
}
app.get('/with-suspense', async (c) => {
return c.html(
Out of Service}>
Loading...}>
)
})
```
## 与 html 集成中间件
¥Integration with html Middleware
结合 JSX 和 html 中间件,实现强大的模板。有关详细信息,请参阅 [html 中间件文档](/docs/helpers/html)。
¥Combine the JSX and html middlewares for powerful templating.
For in-depth details, consult the [html middleware documentation](/docs/helpers/html).
```tsx
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { html } from 'hono/html'
const app = new Hono()
interface SiteData {
title: string
children?: any
}
const Layout = (props: SiteData) =>
html`
${props.title}
${props.children}
`
const Content = (props: { siteData: SiteData; name: string }) => (
Hello {props.name}
)
app.get('/:name', (c) => {
const { name } = c.req.param()
const props = {
name: name,
siteData: {
title: 'JSX with html sample',
},
}
return c.html()
})
export default app
```
## 使用 JSX 渲染器中间件
¥With JSX Renderer Middleware
[JSX 渲染器中间件](/docs/middleware/builtin/jsx-renderer) 允许你更轻松地使用 JSX 创建 HTML 页面。
¥The [JSX Renderer Middleware](/docs/middleware/builtin/jsx-renderer) allows you to create HTML pages more easily with the JSX.
## 覆盖类型定义
¥Override type definitions
你可以覆盖类型定义以添加自定义元素和属性。
¥You can override the type definition to add your custom elements and attributes.
```ts
declare module 'hono/jsx' {
namespace JSX {
interface IntrinsicElements {
'my-custom-element': HTMLAttributes & {
'x-event'?: 'click' | 'scroll'
}
}
}
}
```
# 中间件
¥Middleware
中间件在 Handler 之后/之前工作。我们可以在调度之前获取 `Request`,或者在调度之后操作 `Response`。
¥Middleware works after/before Handler. We can get `Request` before dispatching or manipulate `Response` after dispatching.
## 中间件定义
¥Definition of Middleware
* 处理程序 - 应该返回 `Response` 对象。只会调用一个处理程序。
¥Handler - should return `Response` object. Only one handler will be called.
* 中间件 - 应该不返回任何内容,将继续使用 `await next()` 进行下一个中间件
¥Middleware - should return nothing, will be proceeded to next middleware with `await next()`
用户可以使用 `app.use` 或使用 `app.HTTP_METHOD` 以及处理程序来注册中间件。对于此功能,可以轻松指定路径和方法。
¥The user can register middleware using `app.use` or using `app.HTTP_METHOD` as well as the handlers. For this feature, it's easy to specify the path and the method.
```ts
// match any method, all routes
app.use(logger())
// specify path
app.use('/posts/*', cors())
// specify method and path
app.post('/posts/*', basicAuth())
```
如果处理程序返回 `Response`,它将用于终端用户并停止处理。
¥If the handler returns `Response`, it will be used for the end-user, and stopping the processing.
```ts
app.post('/posts', (c) => c.text('Created!', 201))
```
在这种情况下,在调度之前会处理四个中间件,如下所示:
¥In this case, four middleware are processed before dispatching like this:
```ts
logger() -> cors() -> basicAuth() -> *handler*
```
## 执行顺序
¥Execution order
中间件的执行顺序由其注册的顺序决定。第一个注册的中间件的 `next` 之前的进程首先执行,`next` 之后的进程最后执行。见下文。
¥The order in which Middleware is executed is determined by the order in which it is registered.
The process before the `next` of the first registered Middleware is executed first,
and the process after the `next` is executed last.
See below.
```ts
app.use(async (_, next) => {
console.log('middleware 1 start')
await next()
console.log('middleware 1 end')
})
app.use(async (_, next) => {
console.log('middleware 2 start')
await next()
console.log('middleware 2 end')
})
app.use(async (_, next) => {
console.log('middleware 3 start')
await next()
console.log('middleware 3 end')
})
app.get('/', (c) => {
console.log('handler')
return c.text('Hello!')
})
```
结果如下。
¥Result is the following.
```
middleware 1 start
middleware 2 start
middleware 3 start
handler
middleware 3 end
middleware 2 end
middleware 1 end
```
## 内置中间件
¥Built-in Middleware
Hono 有内置中间件。
¥Hono has built-in middleware.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { poweredBy } from 'hono/powered-by'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
const app = new Hono()
app.use(poweredBy())
app.use(logger())
app.use(
'/auth/*',
basicAuth({
username: 'hono',
password: 'acoolproject',
})
)
```
::: warning 警告
在 Deno 中,可以使用与 Hono 版本不同的中间件版本,但这可能会导致错误。例如,由于版本不同,此代码无法正常工作。
¥In Deno, it is possible to use a different version of middleware than the Hono version, but this can lead to bugs.
For example, this code is not working because the version is different.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'jsr:@hono/hono@4.4.0'
import { upgradeWebSocket } from 'jsr:@hono/hono@4.4.5/deno'
const app = new Hono()
app.get(
'/ws',
upgradeWebSocket(() => ({
// ...
}))
)
```
:::
## 自定义中间件
¥Custom Middleware
你可以在 `app.use()` 中直接编写自己的中间件:
¥You can write your own middleware directly inside `app.use()`:
```ts
// Custom logger
app.use(async (c, next) => {
console.log(`[${c.req.method}] ${c.req.url}`)
await next()
})
// Add a custom header
app.use('/message/*', async (c, next) => {
await next()
c.header('x-message', 'This is middleware!')
})
app.get('/message/hello', (c) => c.text('Hello Middleware!'))
```
但是,将中间件直接嵌入 `app.use()` 会限制其可重用性。因此,我们可以将中间件分成不同的文件。
¥However, embedding middleware directly within `app.use()` can limit its reusability. Therefore, we can separate our
middleware into different files.
为了确保我们不会丢失 `context` 和 `next` 的类型定义,在分离中间件时,我们可以使用 Hono 工厂中的 [`createMiddleware()`](/docs/helpers/factory#createmiddleware)。这也允许我们从下游处理程序安全地键入 [访问我们在 `Context` 中的 `set` 的数据](https://hono.nodejs.cn/docs/api/context#set-get)。
¥To ensure we don't lose type definitions for `context` and `next`, when separating middleware, we can use
[`createMiddleware()`](/docs/helpers/factory#createmiddleware) from Hono's factory. This also allows us to type-safely [access data we've `set` in `Context`](https://hono.nodejs.cn/docs/api/context#set-get) from downstream handlers.
```ts
import { createMiddleware } from 'hono/factory'
const logger = createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
console.log(`[${c.req.method}] ${c.req.url}`)
await next()
})
```
:::info 信息
类型泛型可以与 `createMiddleware` 一起使用:
¥Type generics can be used with `createMiddleware`:
```ts
createMiddleware<{Bindings: Bindings}>(async (c, next) =>
```
:::
### 下一步后修改响应
¥Modify the Response After Next
此外,中间件可以设计为在必要时修改响应:
¥Additionally, middleware can be designed to modify responses if necessary:
```ts
const stripRes = createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
await next()
c.res = undefined
c.res = new Response('New Response')
})
```
## 中间件参数内的上下文访问
¥Context access inside Middleware arguments
要访问中间件参数中的上下文,直接使用 `app.use` 提供的 context 参数即可。有关说明,请参阅下面的示例。
¥To access the context inside middleware arguments, directly use the context parameter provided by `app.use`. See the example below for clarification.
```ts
import { cors } from 'hono/cors'
app.use('*', async (c, next) => {
const middleware = cors({
origin: c.env.CORS_ORIGIN,
})
return middleware(c, next)
})
```
### 扩展中间件中的上下文
¥Extending the Context in Middleware
要扩展中间件内部的上下文,请使用 `c.set`。你可以通过将 `{ Variables: { yourVariable: YourVariableType } }` 泛型参数传递给 `createMiddleware` 函数来使其类型安全。
¥To extend the context inside middleware, use `c.set`. You can make this type-safe by passing a `{ Variables: { yourVariable: YourVariableType } }` generic argument to the `createMiddleware` function.
```ts
import { createMiddleware } from 'hono/factory'
const echoMiddleware = createMiddleware<{
Variables: {
echo: (str: string) => string
}
}>(async (c, next) => {
c.set('echo', (str) => str)
await next()
})
app.get('/echo', echoMiddleware, (c) => {
return c.text(c.var.echo('Hello!'))
})
```
## 第三方中间件
¥Third-party Middleware
内置中间件不依赖于外部模块,但第三方中间件可以依赖于第三方库。因此,有了它们,我们可以制作更复杂的应用。
¥Built-in middleware does not depend on external modules, but third-party middleware can depend on third-party libraries.
So with them, we may make a more complex application.
例如,我们有 GraphQL Server Middleware、Sentry Middleware、Firebase Auth Middleware 等。
¥For example, we have GraphQL Server Middleware, Sentry Middleware, Firebase Auth Middleware, and others.
# 杂项
¥Miscellaneous
## 贡献
¥Contributing
欢迎贡献!你可以通过以下方式做出贡献。
¥Contributions Welcome! You can contribute in the following ways.
* 创建问题 - 提出一个新功能。报告错误。
¥Create an Issue - Propose a new feature. Report a bug.
* 拉取请求 - 修复错误和拼写错误。重构代码。
¥Pull Request - Fix a bug and typo. Refactor the code.
* 创建第三方中间件 - 说明如下。
¥Create third-party middleware - Instruct below.
* 分享 - 在博客、X(Twitter)等上分享你的想法。
¥Share - Share your thoughts on the Blog, X(Twitter), and others.
* 制作你的应用 - 请尝试使用 Hono。
¥Make your application - Please try to use Hono.
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 [贡献指南](https://github.com/honojs/hono/blob/main/docs/CONTRIBUTING.md)。
¥For more details, see [Contribution Guide](https://github.com/honojs/hono/blob/main/docs/CONTRIBUTING.md).
## 赞助
¥Sponsoring
你可以通过 GitHub 赞助计划赞助 Hono 作者。
¥You can sponsor Hono authors via the GitHub sponsor program.
* [GitHub 赞助商 @yusukebe](https://github.com/sponsors/yusukebe)
¥[Sponsor @yusukebe on GitHub Sponsors](https://github.com/sponsors/yusukebe)
* [GitHub 赞助商 @usualoma](https://github.com/sponsors/usualoma)
¥[Sponsor @usualoma on GitHub Sponsors](https://github.com/sponsors/usualoma)
## 其他资源
¥Other Resources
* GitHub 存储库:[https://github.com/honojs](https://github.com/honojs)
¥GitHub repository: [https://github.com/honojs](https://github.com/honojs)
* npm 注册表:[https://www.npmjs.com/package/hono](https://www.npmjs.com/package/hono)
¥npm registry: [https://www.npmjs.com/package/hono](https://www.npmjs.com/package/hono)
* JSR:[https://jsr.io/@hono/hono](https://jsr.io/@hono/hono)
# RPC
RPC 功能允许在服务器和客户端之间共享 API 规范。
¥The RPC feature allows sharing of the API specifications between the server and the client.
首先,从你的服务器代码中导出 `typeof` 你的 Hono 应用(通常称为 `AppType`)— 或者只是你希望客户端可用的路由。
¥First, export the `typeof` your Hono app (commonly called `AppType`)—or just the routes you want available to the client—from your server code.
通过接受 `AppType` 作为通用参数,Hono 客户端可以推断验证器指定的输入类型和返回 `c.json()` 的处理程序发出的输出类型。
¥By accepting `AppType` as a generic parameter, the Hono Client can infer both the input type(s) specified by the Validator, and the output type(s) emitted by handlers returning `c.json()`.
> [!NOTE] 此时,从中间件返回的响应是 [客户端无法推断。](https://github.com/honojs/hono/issues/2719)
>
> ¥[!NOTE]
> At this time, responses returned from middleware are [not inferred by the client.](https://github.com/honojs/hono/issues/2719)
> [!NOTE] 为了使 RPC 类型在 monorepo 中正常工作,在客户端和服务器的 tsconfig.json 文件中,在 `compilerOptions` 中设置 `"strict": true`。[阅读更多。](https://github.com/honojs/hono/issues/2270#issuecomment-2143745118)
>
> ¥[!NOTE]\ For the RPC types to work properly in a monorepo, in both the Client's and Server's tsconfig.json files, set `"strict": true` in `compilerOptions`. [Read more.](https://github.com/honojs/hono/issues/2270#issuecomment-2143745118)
## 服务器
¥Server
你需要在服务器端做的就是编写一个验证器并创建一个变量 `route`。以下示例使用 [Zod Validator](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/zod-validator)。
¥All you need to do on the server side is to write a validator and create a variable `route`. The following example uses [Zod Validator](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/zod-validator).
```ts{1}
const route = app.post(
'/posts',
zValidator(
'form',
z.object({
title: z.string(),
body: z.string(),
})
),
(c) => {
// ...
return c.json(
{
ok: true,
message: 'Created!',
},
201
)
}
)
```
然后,导出类型以与客户端共享 API 规范。
¥Then, export the type to share the API spec with the Client.
```ts
export type AppType = typeof route
```
## 客户端
¥Client
在客户端,首先导入 `hc` 和 `AppType`。
¥On the Client side, import `hc` and `AppType` first.
```ts
import { AppType } from '.'
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
```
`hc` 是一个用于创建客户端的函数。将 `AppType` 作为泛型传递,并将服务器 URL 指定为参数。
¥`hc` is a function to create a client. Pass `AppType` as Generics and specify the server URL as an argument.
```ts
const client = hc('http://localhost:8787/')
```
调用 `client.{path}.{method}` 并将你希望发送到服务器的数据作为参数传递。
¥Call `client.{path}.{method}` and pass the data you wish to send to the server as an argument.
```ts
const res = await client.posts.$post({
form: {
title: 'Hello',
body: 'Hono is a cool project',
},
})
```
`res` 与 "fetch" 响应兼容。你可以使用 `res.json()` 从服务器检索数据。
¥The `res` is compatible with the "fetch" Response. You can retrieve data from the server with `res.json()`.
```ts
if (res.ok) {
const data = await res.json()
console.log(data.message)
}
```
::: warning 文件上传
目前,客户端不支持文件上传。
¥Currently, the client does not support file uploading.
:::
## 状态代码
¥Status code
如果你在 `c.json()` 中明确指定了状态代码,比如 `200` 或 `404`。它将被添加为传递给客户端的类型。
¥If you explicitly specify the status code, such as `200` or `404`, in `c.json()`. It will be added as a type for passing to the client.
```ts
// server.ts
const app = new Hono().get(
'/posts',
zValidator(
'query',
z.object({
id: z.string(),
})
),
async (c) => {
const { id } = c.req.valid('query')
const post: Post | undefined = await getPost(id)
if (post === undefined) {
return c.json({ error: 'not found' }, 404) // Specify 404
}
return c.json({ post }, 200) // Specify 200
}
)
export type AppType = typeof app
```
你可以通过状态代码获取数据。
¥You can get the data by the status code.
```ts
// client.ts
const client = hc('http://localhost:8787/')
const res = await client.posts.$get({
query: {
id: '123',
},
})
if (res.status === 404) {
const data: { error: string } = await res.json()
console.log(data.error)
}
if (res.ok) {
const data: { post: Post } = await res.json()
console.log(data.post)
}
// { post: Post } | { error: string }
type ResponseType = InferResponseType
// { post: Post }
type ResponseType200 = InferResponseType<
typeof client.posts.$get,
200
>
```
## 未找到
¥Not Found
如果要使用客户端,则不应将 `c.notFound()` 用于未找到响应。无法正确推断客户端从服务器获取的数据。
¥If you want to use a client, you should not use `c.notFound()` for the Not Found response. The data that the client gets from the server cannot be inferred correctly.
```ts
// server.ts
export const routes = new Hono().get(
'/posts',
zValidator(
'query',
z.object({
id: z.string(),
})
),
async (c) => {
const { id } = c.req.valid('query')
const post: Post | undefined = await getPost(id)
if (post === undefined) {
return c.notFound() // ❌️
}
return c.json({ post })
}
)
// client.ts
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
const client = hc('/')
const res = await client.posts[':id'].$get({
param: {
id: '123',
},
})
const data = await res.json() // 🙁 data is unknown
```
请使用 `c.json()` 并指定未找到响应的状态代码。
¥Please use `c.json()` and specify the status code for the Not Found Response.
```ts
export const routes = new Hono().get(
'/posts',
zValidator(
'query',
z.object({
id: z.string(),
})
),
async (c) => {
const { id } = c.req.valid('query')
const post: Post | undefined = await getPost(id)
if (post === undefined) {
return c.json({ error: 'not found' }, 404) // Specify 404
}
return c.json({ post }, 200) // Specify 200
}
)
```
## 路径参数
¥Path parameters
你还可以处理包含路径参数的路由。
¥You can also handle routes that include path parameters.
```ts
const route = app.get(
'/posts/:id',
zValidator(
'query',
z.object({
page: z.string().optional(),
})
),
(c) => {
// ...
return c.json({
title: 'Night',
body: 'Time to sleep',
})
}
)
```
使用 `param` 指定你想要包含在路径中的字符串。
¥Specify the string you want to include in the path with `param`.
```ts
const res = await client.posts[':id'].$get({
param: {
id: '123',
},
query: {},
})
```
## Headers
你可以将标头附加到请求中。
¥You can append the headers to the request.
```ts
const res = await client.search.$get(
{
//...
},
{
headers: {
'X-Custom-Header': 'Here is Hono Client',
'X-User-Agent': 'hc',
},
}
)
```
要为所有请求添加通用标头,请将其作为参数指定给 `hc` 函数。
¥To add a common header to all requests, specify it as an argument to the `hc` function.
```ts
const client = hc('/api', {
headers: {
Authorization: 'Bearer TOKEN',
},
})
```
## `init` 选项
¥`init` option
你可以将 fetch 的 `RequestInit` 对象作为 `init` 选项传递给请求。下面是中止请求的示例。
¥You can pass the fetch's `RequestInit` object to the request as the `init` option. Below is an example of aborting a Request.
```ts
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
const client = hc('http://localhost:8787/')
const abortController = new AbortController()
const res = await client.api.posts.$post(
{
json: {
// Request body
},
},
{
// RequestInit object
init: {
signal: abortController.signal,
},
}
)
// ...
abortController.abort()
```
::: info 信息
由 `init` 定义的 `RequestInit` 对象具有最高优先级。它可用于覆盖由其他选项(如 `body | method | headers`)设置的内容。
¥A `RequestInit` object defined by `init` takes the highest priority. It could be used to overwrite things set by other options like `body | method | headers`.
:::
## `$url()`
你可以使用 `$url()` 获取用于访问端点的 `URL` 对象。
¥You can get a `URL` object for accessing the endpoint by using `$url()`.
::: warning 警告
你必须传入绝对 URL 才能使其工作。传入相对 URL `/` 将导致以下错误。
¥You have to pass in an absolute URL for this to work. Passing in a relative URL `/` will result in the following error.
`Uncaught TypeError: Failed to construct 'URL': Invalid URL`
```ts
// ❌ Will throw error
const client = hc('/')
client.api.post.$url()
// ✅ Will work as expected
const client = hc('http://localhost:8787/')
client.api.post.$url()
```
:::
```ts
const route = app
.get('/api/posts', (c) => c.json({ posts }))
.get('/api/posts/:id', (c) => c.json({ post }))
const client = hc('http://localhost:8787/')
let url = client.api.posts.$url()
console.log(url.pathname) // `/api/posts`
url = client.api.posts[':id'].$url({
param: {
id: '123',
},
})
console.log(url.pathname) // `/api/posts/123`
```
## 自定义 `fetch` 方法
¥Custom `fetch` method
你可以设置自定义 `fetch` 方法。
¥You can set the custom `fetch` method.
在下面的 Cloudflare Worker 示例脚本中,使用了 Service Bindings 的 `fetch` 方法,而不是默认的 `fetch`。
¥In the following example script for Cloudflare Worker, the Service Bindings' `fetch` method is used instead of the default `fetch`.
```toml
# wrangler.toml
services = [
{ binding = "AUTH", service = "auth-service" },
]
```
```ts
// src/client.ts
const client = hc('/', {
fetch: c.env.AUTH.fetch.bind(c.env.AUTH),
})
```
## 推断
¥Infer
使用 `InferRequestType` 和 `InferResponseType` 来了解要请求的对象类型和要返回的对象类型。
¥Use `InferRequestType` and `InferResponseType` to know the type of object to be requested and the type of object to be returned.
```ts
import type { InferRequestType, InferResponseType } from 'hono/client'
// InferRequestType
const $post = client.todo.$post
type ReqType = InferRequestType['form']
// InferResponseType
type ResType = InferResponseType
```
## 使用 SWR
¥Using SWR
你还可以使用 React Hook 库,例如 [SWR](https://swr.nodejs.cn)。
¥You can also use a React Hook library such as [SWR](https://swr.nodejs.cn).
```tsx
import useSWR from 'swr'
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
import type { InferRequestType } from 'hono/client'
import { AppType } from '../functions/api/[[route]]'
const App = () => {
const client = hc('/api')
const $get = client.hello.$get
const fetcher =
(arg: InferRequestType) => async () => {
const res = await $get(arg)
return await res.json()
}
const { data, error, isLoading } = useSWR(
'api-hello',
fetcher({
query: {
name: 'SWR',
},
})
)
if (error) return
failed to load
if (isLoading) return
loading...
return
{data?.message}
}
export default App
```
## 在更大的应用中使用 RPC
¥Using RPC with larger applications
对于较大的应用,例如 [构建更大的应用](/docs/guides/best-practices#building-a-larger-application) 中提到的示例,需要注意推断的类型。一种简单的方法是链接处理程序,以便始终推断类型。
¥In the case of a larger application, such as the example mentioned in [Building a larger application](/docs/guides/best-practices#building-a-larger-application), you need to be careful about the type of inference.
A simple way to do this is to chain the handlers so that the types are always inferred.
```ts
// authors.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
.get('/', (c) => c.json('list authors'))
.post('/', (c) => c.json('create an author', 201))
.get('/:id', (c) => c.json(`get ${c.req.param('id')}`))
export default app
```
```ts
// books.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
.get('/', (c) => c.json('list books'))
.post('/', (c) => c.json('create a book', 201))
.get('/:id', (c) => c.json(`get ${c.req.param('id')}`))
export default app
```
然后,你可以像平常一样导入子路由,并确保也链接它们的处理程序,因为这是应用的顶层(在本例中),这是我们想要导出的类型。
¥You can then import the sub-routers as you usually would, and make sure you chain their handlers as well, since this is the top level of the app in this case, this is the type we'll want to export.
```ts
// index.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import authors from './authors'
import books from './books'
const app = new Hono()
const routes = app.route('/authors', authors).route('/books', books)
export default app
export type AppType = typeof routes
```
你现在可以使用已注册的 AppType 创建新客户端并像平常一样使用它。
¥You can now create a new client using the registered AppType and use it as you would normally.
## 已知问题
¥Known issues
### IDE 性能
¥IDE performance
使用 RPC 时,路由越多,IDE 就会变得越慢。其中一个主要原因是执行了大量类型实例化来推断应用的类型。
¥When using RPC, the more routes you have, the slower your IDE will become. One of the main reasons for this is that massive amounts of type instantiations are executed to infer the type of your app.
例如,假设你的应用有这样的路由:
¥For example, suppose your app has a route like this:
```ts
// app.ts
export const app = new Hono().get('foo/:id', (c) =>
c.json({ ok: true }, 200)
)
```
Hono 将推断类型如下:
¥Hono will infer the type as follows:
```ts
export const app = Hono().get<
'foo/:id',
'foo/:id',
JSONRespondReturn<{ ok: boolean }, 200>,
BlankInput,
BlankEnv
>('foo/:id', (c) => c.json({ ok: true }, 200))
```
这是单个路由的类型实例化。虽然用户不需要手动编写这些类型参数,这是一件好事,但众所周知类型实例化需要花费很多时间。每次使用应用时,IDE 中使用的 `tsserver` 都会执行这项耗时的任务。如果你有很多路由,这会显著降低你的 IDE 速度。
¥This is a type instantiation for a single route. While the user doesn't need to write these type arguments manually, which is a good thing, it's known that type instantiation takes much time. `tsserver` used in your IDE does this time consuming task every time you use the app. If you have a lot of routes, this can slow down your IDE significantly.
但是,我们有一些技巧可以缓解这个问题。
¥However, we have some tips to mitigate this issue.
#### Hono 版本不匹配
¥Hono version mismatch
如果你的后端与前端分开并且位于不同的目录中,则需要确保 Hono 版本匹配。如果你在后端使用一个 Hono 版本,在前端使用另一个版本,则会遇到诸如 "类型实例化过深且可能无限" 之类的问题。
¥If your backend is separate from the frontend and lives in a different directory, you need to ensure that the Hono versions match. If you use one Hono version on the backend and another on the frontend, you'll run into issues such as "*Type instantiation is excessively deep and possibly infinite*".

#### TypeScript 项目参考
¥TypeScript project references
与 [Hono 版本不匹配](#hono-version-mismatch) 的情况一样,如果你的后端和前端是分开的,你会遇到问题。如果要在前端从后端(例如 `AppType`)访问代码,则需要使用 [项目参考](https://ts.nodejs.cn/docs/handbook/project-references.html)。TypeScript 的项目引用允许一个 TypeScript 代码库访问和使用来自另一个 TypeScript 代码库的代码。(来源:[Hono RPC 和 TypeScript 项目参考](https://catalins.tech/hono-rpc-in-monorepos/))。
¥Like in the case of [Hono version mismatch](#hono-version-mismatch), you'll run into issues if your backend and frontend are separate. If you want to access code from the backend (`AppType`, for example) on the frontend, you need to use [project references](https://ts.nodejs.cn/docs/handbook/project-references.html). TypeScript's project references allow one TypeScript codebase to access and use code from another TypeScript codebase. *(source: [Hono RPC And TypeScript Project References](https://catalins.tech/hono-rpc-in-monorepos/))*.
#### 使用代码前先编译(推荐)
¥Compile your code before using it (recommended)
`tsc` 可以在编译时执行类型实例化等繁重任务!然后,每次使用 `tsserver` 时,它不需要实例化所有类型参数。它将使你的 IDE 更快!
¥`tsc` can do heavy tasks like type instantiation at compile time! Then, `tsserver` doesn't need to instantiate all the type arguments every time you use it. It will make your IDE a lot faster!
编译包括服务器应用在内的客户端可为你提供最佳性能。将以下代码放入你的项目中:
¥Compiling your client including the server app gives you the best performance. Put the following code in your project:
```ts
import { app } from './app'
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
// this is a trick to calculate the type when compiling
const client = hc('')
export type Client = typeof client
export const hcWithType = (...args: Parameters): Client =>
hc(...args)
```
编译后,你可以使用 `hcWithType` 而不是 `hc` 来获取已计算类型的客户端。
¥After compiling, you can use `hcWithType` instead of `hc` to get the client with the type already calculated.
```ts
const client = hcWithType('http://localhost:8787/')
const res = await client.posts.$post({
form: {
title: 'Hello',
body: 'Hono is a cool project',
},
})
```
如果你的项目是 monorepo,则此解决方案确实很合适。使用 [`turborepo`](https://turbo.build/repo/docs) 这样的工具,你可以轻松地分离服务器项目和客户端项目,并通过管理它们之间的依赖获得更好的集成。这是 [工作示例](https://github.com/m-shaka/hono-rpc-perf-tips-example)。
¥If your project is a monorepo, this solution does fit well. Using a tool like [`turborepo`](https://turbo.build/repo/docs), you can easily separate the server project and the client project and get better integration managing dependencies between them. Here is [a working example](https://github.com/m-shaka/hono-rpc-perf-tips-example).
你还可以使用 `concurrently` 或 `npm-run-all` 等工具手动协调构建过程。
¥You can also coordinate your build process manually with tools like `concurrently` or `npm-run-all`.
#### 手动指定类型参数
¥Specify type arguments manually
这有点麻烦,但你可以手动指定类型参数以避免类型实例化。
¥This is a bit cumbersome, but you can specify type arguments manually to avoid type instantiation.
```ts
const app = new Hono().get<'foo/:id'>('foo/:id', (c) =>
c.json({ ok: true }, 200)
)
```
仅指定单一类型参数会对性能产生影响,而如果你有很多路由,则可能会花费大量时间和精力。
¥Specifying just single type argument make a difference in performance, while it may take you a lot of time and effort if you have a lot of routes.
#### 将你的应用和客户端拆分为多个文件
¥Split your app and client into multiple files
如 [在更大的应用中使用 RPC](#using-rpc-with-larger-applications) 中所述,你可以将应用拆分为多个应用。你还可以为每个应用创建一个客户端:
¥As described in [Using RPC with larger applications](#using-rpc-with-larger-applications), you can split your app into multiple apps. You can also create a client for each app:
```ts
// authors-cli.ts
import { app as authorsApp } from './authors'
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
const authorsClient = hc('/authors')
// books-cli.ts
import { app as booksApp } from './books'
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
const booksClient = hc('/books')
```
这样,`tsserver` 就不需要一次实例化所有路由的类型了。
¥This way, `tsserver` doesn't need to instantiate types for all routes at once.
# 测试
¥Testing
测试很重要。实际上,测试 Hono 的应用很容易。创建测试环境的方式因每个运行时而异,但基本步骤相同。在本节中,让我们使用 Cloudflare Workers 和 Jest 进行测试。
¥Testing is important.
In actuality, it is easy to test Hono's applications.
The way to create a test environment differs from each runtime, but the basic steps are the same.
In this section, let's test with Cloudflare Workers and Jest.
## 请求和响应
¥Request and Response
你所要做的就是创建一个请求并将其传递给 Hono 应用以验证响应。你可以使用 `app.request` 的有用方法。
¥All you do is create a Request and pass it to the Hono application to validate the Response.
And, you can use `app.request` the useful method.
::: tip 提示
对于类型测试客户端,请参阅 [测试助手](/docs/helpers/testing)。
¥For a typed test client see the [testing helper](/docs/helpers/testing).
:::
例如,考虑一个提供以下 REST API 的应用。
¥For example, consider an application that provides the following REST API.
```ts
app.get('/posts', (c) => {
return c.text('Many posts')
})
app.post('/posts', (c) => {
return c.json(
{
message: 'Created',
},
201,
{
'X-Custom': 'Thank you',
}
)
})
```
向 `GET /posts` 发出请求并测试响应。
¥Make a request to `GET /posts` and test the response.
```ts
describe('Example', () => {
test('GET /posts', async () => {
const res = await app.request('/posts')
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
expect(await res.text()).toBe('Many posts')
})
})
```
要向 `POST /posts` 发出请求,请执行以下操作。
¥To make a request to `POST /posts`, do the following.
```ts
test('POST /posts', async () => {
const res = await app.request('/posts', {
method: 'POST',
})
expect(res.status).toBe(201)
expect(res.headers.get('X-Custom')).toBe('Thank you')
expect(await res.json()).toEqual({
message: 'Created',
})
})
```
要使用 `JSON` 数据向 `POST /posts` 发出请求,请执行以下操作。
¥To make a request to `POST /posts` with `JSON` data, do the following.
```ts
test('POST /posts', async () => {
const res = await app.request('/posts', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ message: 'hello hono' }),
headers: new Headers({ 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }),
})
expect(res.status).toBe(201)
expect(res.headers.get('X-Custom')).toBe('Thank you')
expect(await res.json()).toEqual({
message: 'Created',
})
})
```
要使用 `multipart/form-data` 数据向 `POST /posts` 发出请求,请执行以下操作。
¥To make a request to `POST /posts` with `multipart/form-data` data, do the following.
```ts
test('POST /posts', async () => {
const formData = new FormData()
formData.append('message', 'hello')
const res = await app.request('/posts', {
method: 'POST',
body: formData,
})
expect(res.status).toBe(201)
expect(res.headers.get('X-Custom')).toBe('Thank you')
expect(await res.json()).toEqual({
message: 'Created',
})
})
```
你还可以传递 Request 类的实例。
¥You can also pass an instance of the Request class.
```ts
test('POST /posts', async () => {
const req = new Request('http://localhost/posts', {
method: 'POST',
})
const res = await app.request(req)
expect(res.status).toBe(201)
expect(res.headers.get('X-Custom')).toBe('Thank you')
expect(await res.json()).toEqual({
message: 'Created',
})
})
```
通过这种方式,你可以像端到端一样对其进行测试。
¥In this way, you can test it as like an End-to-End.
## Env
要设置 `c.env` 进行测试,你可以将其作为第 3 个参数传递给 `app.request`。这对于模拟 [Cloudflare Workers Bindings](https://hono.nodejs.cn/getting-started/cloudflare-workers#bindings) 之类的值很有用:
¥To set `c.env` for testing, you can pass it as the 3rd parameter to `app.request`. This is useful for mocking values like [Cloudflare Workers Bindings](https://hono.nodejs.cn/getting-started/cloudflare-workers#bindings):
```ts
const MOCK_ENV = {
API_HOST: 'example.com',
DB: {
prepare: () => {
/* mocked D1 */
},
},
}
test('GET /posts', async () => {
const res = await app.request('/posts', {}, MOCK_ENV)
})
```
# 验证
¥Validation
Hono 只提供了一个非常薄的验证器。但是,当与第三方验证器结合使用时,它会非常强大。此外,RPC 功能允许你通过类型与客户端共享 API 规范。
¥Hono provides only a very thin Validator.
But, it can be powerful when combined with a third-party Validator.
In addition, the RPC feature allows you to share API specifications with your clients through types.
## 手动验证器
¥Manual validator
首先,引入一种无需使用第三方验证器即可验证传入值的方法。
¥First, introduce a way to validate incoming values without using the third-party Validator.
从 `hono/validator` 导入 `validator`。
¥Import `validator` from `hono/validator`.
```ts
import { validator } from 'hono/validator'
```
要验证表单数据,请将 `form` 指定为第一个参数,并将回调指定为第二个参数。在回调中,验证值并在最后返回验证后的值。`validator` 可以用作中间件。
¥To validate form data, specify `form` as the first argument and a callback as the second argument.
In the callback, validates the value and return the validated values at the end.
The `validator` can be used as middleware.
```ts
app.post(
'/posts',
validator('form', (value, c) => {
const body = value['body']
if (!body || typeof body !== 'string') {
return c.text('Invalid!', 400)
}
return {
body: body,
}
}),
//...
```
在处理程序中,你可以使用 `c.req.valid('form')` 获取经过验证的值。
¥Within the handler you can get the validated value with `c.req.valid('form')`.
```ts
, (c) => {
const { body } = c.req.valid('form')
// ... do something
return c.json(
{
message: 'Created!',
},
201
)
}
```
除了 `form` 之外,验证目标还包括 `json`、`query`、`header`、`param` 和 `cookie`。
¥Validation targets include `json`, `query`, `header`, `param` and `cookie` in addition to `form`.
::: warning 警告
验证 `json` 时,请求必须包含 `Content-Type: application/json` 标头,否则请求正文将无法解析,你将收到警告。
¥When you validate `json`, the request *must* contain a `Content-Type: application/json` header
otherwise the request body will not be parsed and you will receive a warning.
使用 [`app.request()`](../api/request.md) 进行测试时,设置 `content-type` 标头非常重要。
¥It is important to set the `content-type` header when testing using
[`app.request()`](../api/request.md).
给定一个这样的应用。
¥Given an application like this.
```ts
const app = new Hono()
app.post(
'/testing',
validator('json', (value, c) => {
// pass-through validator
return value
}),
(c) => {
const body = c.req.valid('json')
return c.json(body)
}
)
```
你的测试可以这样写。
¥Your tests can be written like this.
```ts
// ❌ this will not work
const res = await app.request('/testing', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ key: 'value' }),
})
const data = await res.json()
console.log(data) // undefined
// ✅ this will work
const res = await app.request('/testing', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({ key: 'value' }),
headers: new Headers({ 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }),
})
const data = await res.json()
console.log(data) // { key: 'value' }
```
:::
::: warning 警告
验证 `header` 时,你需要使用小写名称作为键。
¥When you validate `header`, you need to use **lowercase** name as the key.
如果要验证 `Idempotency-Key` 标头,则需要使用 `idempotency-key` 作为密钥。
¥If you want to validate the `Idempotency-Key` header, you need to use `idempotency-key` as the key.
```ts
// ❌ this will not work
app.post(
'/api',
validator('header', (value, c) => {
// idempotencyKey is always undefined
// so this middleware always return 400 as not expected
const idempotencyKey = value['Idempotency-Key']
if (idempotencyKey == undefined || idempotencyKey === '') {
throw HTTPException(400, {
message: 'Idempotency-Key is required',
})
}
return { idempotencyKey }
}),
(c) => {
const { idempotencyKey } = c.req.valid('header')
// ...
}
)
// ✅ this will work
app.post(
'/api',
validator('header', (value, c) => {
// can retrieve the value of the header as expected
const idempotencyKey = value['idempotency-key']
if (idempotencyKey == undefined || idempotencyKey === '') {
throw HTTPException(400, {
message: 'Idempotency-Key is required',
})
}
return { idempotencyKey }
}),
(c) => {
const { idempotencyKey } = c.req.valid('header')
// ...
}
)
```
:::
## 多个验证器
¥Multiple validators
你还可以包含多个验证器来验证请求的不同部分:
¥You can also include multiple validators to validate different parts of request:
```ts
app.post(
'/posts/:id',
validator('param', ...),
validator('query', ...),
validator('json', ...),
(c) => {
//...
}
```
## 使用 Zod
¥With Zod
你可以使用第三方验证器之一 [Zod](https://zod.nodejs.cn)。我们建议使用第三方验证器。
¥You can use [Zod](https://zod.nodejs.cn), one of third-party validators.
We recommend using a third-party validator.
从 Npm 注册表安装。
¥Install from the Npm registry.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i zod
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add zod
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add zod
```
```sh [bun]
bun add zod
```
:::
从 `zod` 导入 `z`。
¥Import `z` from `zod`.
```ts
import { z } from 'zod'
```
编写你的模式。
¥Write your schema.
```ts
const schema = z.object({
body: z.string(),
})
```
你可以在回调函数中使用模式进行验证并返回验证后的值。
¥You can use the schema in the callback function for validation and return the validated value.
```ts
const route = app.post(
'/posts',
validator('form', (value, c) => {
const parsed = schema.safeParse(value)
if (!parsed.success) {
return c.text('Invalid!', 401)
}
return parsed.data
}),
(c) => {
const { body } = c.req.valid('form')
// ... do something
return c.json(
{
message: 'Created!',
},
201
)
}
)
```
## Zod 验证器中间件
¥Zod Validator Middleware
你可以使用 [Zod 验证器中间件](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/zod-validator) 使其更加容易。
¥You can use the [Zod Validator Middleware](https://github.com/honojs/middleware/tree/main/packages/zod-validator) to make it even easier.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i @hono/zod-validator
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add @hono/zod-validator
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add @hono/zod-validator
```
```sh [bun]
bun add @hono/zod-validator
```
:::
并导入 `zValidator`。
¥And import `zValidator`.
```ts
import { zValidator } from '@hono/zod-validator'
```
并按如下方式编写。
¥And write as follows.
```ts
const route = app.post(
'/posts',
zValidator(
'form',
z.object({
body: z.string(),
})
),
(c) => {
const validated = c.req.valid('form')
// ... use your validated data
}
)
```
# 阿里云函数计算
¥Alibaba Cloud Function Compute
[阿里云函数计算](https://www.alibabacloud.com/en/product/function-compute) 是一种完全托管的、事件驱动的计算服务。函数计算允许你专注于编写和上传代码,而无需管理服务器等基础设施。
¥[Alibaba Cloud Function Compute](https://www.alibabacloud.com/en/product/function-compute) is a fully managed, event-driven compute service. Function Compute allows you to focus on writing and uploading code without having to manage infrastructure such as servers.
本指南使用第三方适配器 [rwv/hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter](https://github.com/rwv/hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter) 在阿里云函数计算上运行 Hono。
¥This guide uses a third-party adapter [rwv/hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter](https://github.com/rwv/hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter) to run Hono on Alibaba Cloud Function Compute.
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
npm i hono hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter
npm i -D @serverless-devs/s esbuild
mkdir src
touch src/index.ts
```
```sh [yarn]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
yarn add hono hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter
yarn add -D @serverless-devs/s esbuild
mkdir src
touch src/index.ts
```
```sh [pnpm]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
pnpm add hono hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter
pnpm add -D @serverless-devs/s esbuild
mkdir src
touch src/index.ts
```
```sh [bun]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
bun add hono hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter
bun add -D esbuild @serverless-devs/s
mkdir src
touch src/index.ts
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `src/index.ts`。
¥Edit `src/index.ts`.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono-alibaba-cloud-fc3-adapter'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Hono!'))
export const handler = handle(app)
```
## 3. 设置 serverless-devs
¥ Setup serverless-devs
> [serverless-devs](https://github.com/Serverless-Devs/Serverless-Devs) 是一个开源的开放式无服务器开发者平台,致力于为开发者提供强大的工具链系统。通过该平台,开发者不仅可以一键体验多云无服务器产品、快速部署无服务器项目,还可以在无服务器应用的全生命周期中管理项目,并非常简单快捷地将无服务器开发与其他工具/平台结合起来,进一步提高研发和运维的效率。
>
> ¥[serverless-devs](https://github.com/Serverless-Devs/Serverless-Devs) is an open source and open serverless developer platform dedicated to providing developers with a powerful tool chain system. Through this platform, developers can not only experience multi cloud serverless products with one click and rapidly deploy serverless projects, but also manage projects in the whole life cycle of serverless applications, and combine serverless devs with other tools / platforms very simply and quickly to further improve the efficiency of R & D, operation and maintenance.
添加阿里云 AccessKeyID 和 AccessKeySecret
¥Add the Alibaba Cloud AccessKeyID & AccessKeySecret
```sh
npx s config add
# Please select a provider: Alibaba Cloud (alibaba)
# Input your AccessKeyID & AccessKeySecret
```
编辑 `s.yaml`
¥Edit `s.yaml`
```yaml
edition: 3.0.0
name: my-app
access: 'default'
vars:
region: 'us-west-1'
resources:
my-app:
component: fc3
props:
region: ${vars.region}
functionName: 'my-app'
description: 'Hello World by Hono'
runtime: 'nodejs20'
code: ./dist
handler: index.handler
memorySize: 1024
timeout: 300
```
编辑 `package.json` 中的 `scripts` 部分:
¥Edit `scripts` section in `package.json`:
```json
{
"scripts": {
"build": "esbuild --bundle --outfile=./dist/index.js --platform=node --target=node20 ./src/index.ts",
"deploy": "s deploy -y"
}
}
```
## 4. 部署
¥ Deploy
最后,运行命令进行部署:
¥Finally, run the command to deploy:
```sh
npm run build # Compile the TypeScript code to JavaScript
npm run deploy # Deploy the function to Alibaba Cloud Function Compute
```
# AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda 是 Amazon Web Services 提供的无服务器平台。你可以运行代码以响应事件并自动为你管理底层计算资源。
¥AWS Lambda is a serverless platform by Amazon Web Services.
You can run your code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying compute resources for you.
Hono 在 Node.js 18+ 环境中在 AWS Lambda 上运行。
¥Hono works on AWS Lambda with the Node.js 18+ environment.
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
在 AWS Lambda 上创建应用时,[CDK](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/serverless-cdk.html) 可用于设置 IAM 角色、API 网关等功能。
¥When creating the application on AWS Lambda,
[CDK](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/serverless-cdk.html)
is useful to setup the functions such as IAM Role, API Gateway, and others.
使用 `cdk` CLI 初始化你的项目。
¥Initialize your project with the `cdk` CLI.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
npm i hono
mkdir lambda
touch lambda/index.ts
```
```sh [yarn]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
yarn add hono
mkdir lambda
touch lambda/index.ts
```
```sh [pnpm]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
pnpm add hono
mkdir lambda
touch lambda/index.ts
```
```sh [bun]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
bun add hono
mkdir lambda
touch lambda/index.ts
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `lambda/index.ts`。
¥Edit `lambda/index.ts`.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/aws-lambda'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Hono!'))
export const handler = handle(app)
```
## 3. 部署
¥ Deploy
编辑 `lib/cdk-stack.ts`。
¥Edit `lib/cdk-stack.ts`.
```ts
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'
import { Construct } from 'constructs'
import * as lambda from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda'
import * as apigw from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-apigateway'
import { NodejsFunction } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda-nodejs'
export class MyAppStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props)
const fn = new NodejsFunction(this, 'lambda', {
entry: 'lambda/index.ts',
handler: 'handler',
runtime: lambda.Runtime.NODEJS_20_X,
})
fn.addFunctionUrl({
authType: lambda.FunctionUrlAuthType.NONE,
})
new apigw.LambdaRestApi(this, 'myapi', {
handler: fn,
})
}
}
```
最后,运行命令进行部署:
¥Finally, run the command to deploy:
```sh
cdk deploy
```
## 提供二进制数据
¥Serve Binary data
Hono 支持二进制数据作为响应。在 Lambda 中,需要使用 base64 编码才能返回二进制数据。将二进制类型设置为 `Content-Type` 标头后,Hono 会自动将数据编码为 base64。
¥Hono supports binary data as a response.
In Lambda, base64 encoding is required to return binary data.
Once binary type is set to `Content-Type` header, Hono automatically encodes data to base64.
```ts
app.get('/binary', async (c) => {
// ...
c.status(200)
c.header('Content-Type', 'image/png') // means binary data
return c.body(buffer) // supports `ArrayBufferLike` type, encoded to base64.
})
```
## 访问 AWS Lambda 对象
¥Access AWS Lambda Object
在 Hono 中,你可以通过绑定 `LambdaEvent`、`LambdaContext` 类型并使用 `c.env` 来访问 AWS Lambda 事件和上下文
¥In Hono, you can access the AWS Lambda Events and Context by binding the `LambdaEvent`, `LambdaContext` type and using `c.env`
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import type { LambdaEvent, LambdaContext } from 'hono/aws-lambda'
import { handle } from 'hono/aws-lambda'
type Bindings = {
event: LambdaEvent
lambdaContext: LambdaContext
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get('/aws-lambda-info/', (c) => {
return c.json({
isBase64Encoded: c.env.event.isBase64Encoded,
awsRequestId: c.env.lambdaContext.awsRequestId,
})
})
export const handler = handle(app)
```
## 访问 RequestContext
¥Access RequestContext
在 Hono 中,你可以通过绑定 `LambdaEvent` 类型并使用 `c.env.event.requestContext` 来访问 AWS Lambda 请求上下文。
¥In Hono, you can access the AWS Lambda request context by binding the `LambdaEvent` type and using `c.env.event.requestContext`.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import type { LambdaEvent } from 'hono/aws-lambda'
import { handle } from 'hono/aws-lambda'
type Bindings = {
event: LambdaEvent
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get('/custom-context/', (c) => {
const lambdaContext = c.env.event.requestContext
return c.json(lambdaContext)
})
export const handler = handle(app)
```
### v3.10.0 之前(已弃用)
¥Before v3.10.0 (deprecated)
你可以通过绑定 `ApiGatewayRequestContext` 类型并使用 `c.env.` 来访问 AWS Lambda 请求上下文
¥you can access the AWS Lambda request context by binding the `ApiGatewayRequestContext` type and using `c.env.`
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import type { ApiGatewayRequestContext } from 'hono/aws-lambda'
import { handle } from 'hono/aws-lambda'
type Bindings = {
requestContext: ApiGatewayRequestContext
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get('/custom-context/', (c) => {
const lambdaContext = c.env.requestContext
return c.json(lambdaContext)
})
export const handler = handle(app)
```
## Lambda 响应流
¥Lambda response streaming
通过更改 AWS Lambda 的调用模式,你可以实现 [流式响应](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/introducing-aws-lambda-response-streaming/)。
¥By changing the invocation mode of AWS Lambda, you can achieve [Streaming Response](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/introducing-aws-lambda-response-streaming/).
```diff
fn.addFunctionUrl({
authType: lambda.FunctionUrlAuthType.NONE,
+ invokeMode: lambda.InvokeMode.RESPONSE_STREAM,
})
```
通常,实现需要使用 awslambda.streamifyResponse 将块写入 NodeJS.WritableStream,但使用 AWS Lambda Adaptor,你可以使用 streamHandle 而不是 handle 来实现 Hono 的传统流式响应。
¥Typically, the implementation requires writing chunks to NodeJS.WritableStream using awslambda.streamifyResponse, but with the AWS Lambda Adaptor, you can achieve the traditional streaming response of Hono by using streamHandle instead of handle.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { streamHandle } from 'hono/aws-lambda'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/stream', async (c) => {
return streamText(c, async (stream) => {
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
await stream.writeln(`${i}`)
await stream.sleep(1)
}
})
})
const handler = streamHandle(app)
```
# Azure 函数
¥Azure Functions
[Azure 函数](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/functions) 是来自 Microsoft Azure 的无服务器平台。你可以运行代码以响应事件,它会自动为你管理底层计算资源。
¥[Azure Functions](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/functions) is a serverless platform from Microsoft Azure. You can run your code in response to events, and it automatically manages the underlying compute resources for you.
Hono 最初并不是为 Azure Functions 设计的。但使用 [Azure Functions 适配器](https://github.com/Marplex/hono-azurefunc-adapter) 它也可以在它上面运行。
¥Hono was not designed for Azure Functions at first. But with [Azure Functions Adapter](https://github.com/Marplex/hono-azurefunc-adapter) it can run on it as well.
它适用于在 Node.js 18 或更高版本上运行的 Azure Functions V4。
¥It works with Azure Functions **V4** running on Node.js 18 or above.
## 1. 安装 CLI
¥ Install CLI
要创建 Azure 函数,必须先安装 [Azure Functions 核心工具](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/create-first-function-cli-typescript?pivots=nodejs-model-v4#install-the-azure-functions-core-tools)。
¥To create an Azure Function, you must first install [Azure Functions Core Tools](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/create-first-function-cli-typescript?pivots=nodejs-model-v4#install-the-azure-functions-core-tools).
在 macOS 上
¥On macOS
```sh
brew tap azure/functions
brew install azure-functions-core-tools@4
```
其他操作系统请点击此链接:
¥Follow this link for other OS:
* [安装 Azure Functions Core 工具 | Microsoft Learn](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/create-first-function-cli-typescript?pivots=nodejs-model-v4#install-the-azure-functions-core-tools)
¥[Install the Azure Functions Core Tools | Microsoft Learn](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/create-first-function-cli-typescript?pivots=nodejs-model-v4#install-the-azure-functions-core-tools)
## 2. 设置
¥ Setup
在当前文件夹中创建一个 TypeScript Node.js V4 项目。
¥Create a TypeScript Node.js V4 project in the current folder.
```sh
func init --typescript
```
更改主机的默认路由前缀。将此属性添加到 `host.json` 的根 json 对象:
¥Change the default route prefix of the host. Add this property to the root json object of `host.json`:
```json
"extensions": {
"http": {
"routePrefix": ""
}
}
```
::: info 信息
默认的 Azure Functions 路由前缀为 `/api`。如果你不按照上面那样改的话,一定要确保所有 Hono 路由都以 `/api` 开头
¥The default Azure Functions route prefix is `/api`. If you don't change it as shown above, be sure to start all your Hono routes with `/api`
:::
现在你已准备好安装 Hono 和 Azure Functions Adapter:
¥Now you are ready to install Hono and the Azure Functions Adapter with:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i @marplex/hono-azurefunc-adapter hono
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add @marplex/hono-azurefunc-adapter hono
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add @marplex/hono-azurefunc-adapter hono
```
```sh [bun]
bun add @marplex/hono-azurefunc-adapter hono
```
:::
## 3. Hello World
创建 `src/app.ts`:
¥Create `src/app.ts`:
```ts
// src/app.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Azure Functions!'))
export default app
```
创建 `src/functions/httpTrigger.ts`:
¥Create `src/functions/httpTrigger.ts`:
```ts
// src/functions/httpTrigger.ts
import { app } from '@azure/functions'
import { azureHonoHandler } from '@marplex/hono-azurefunc-adapter'
import honoApp from '../app'
app.http('httpTrigger', {
methods: [
//Add all your supported HTTP methods here
'GET',
'POST',
'DELETE',
'PUT',
],
authLevel: 'anonymous',
route: '{*proxy}',
handler: azureHonoHandler(honoApp.fetch),
})
```
## 4. 运行
¥ Run
在本地运行开发服务器。然后,在你的 Web 浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:7071`。
¥Run the development server locally. Then, access `http://localhost:7071` in your Web browser.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run start
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn start
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm start
```
```sh [bun]
bun run start
```
:::
## 5. 部署
¥ Deploy
::: info 信息
在部署到 Azure 之前,你需要在云基础架构中创建一些资源。请访问有关 [为你的函数创建支持 Azure 资源](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/create-first-function-cli-typescript?pivots=nodejs-model-v4\&tabs=windows%2Cazure-cli%2Cbrowser#create-supporting-azure-resources-for-your-function) 的 Microsoft 文档
¥Before you can deploy to Azure, you need to create some resources in your cloud infrastructure. Please visit the Microsoft documentation on [Create supporting Azure resources for your function](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/create-first-function-cli-typescript?pivots=nodejs-model-v4\&tabs=windows%2Cazure-cli%2Cbrowser#create-supporting-azure-resources-for-your-function)
:::
构建项目以进行部署:
¥Build the project for deployment:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run build
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn build
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm build
```
```sh [bun]
bun run build
```
:::
将你的项目部署到 Azure Cloud 中的函数应用。将 `` 替换为你的应用名称。
¥Deploy your project to the function app in Azure Cloud. Replace `` with the name of your app.
```sh
func azure functionapp publish
```
# 入门
¥Getting Started
使用 Hono 非常简单。我们可以设置项目、编写代码、使用本地服务器进行开发并快速部署。相同的代码可以在任何运行时上运行,只是入口点不同。让我们看看 Hono 的基本用法。
¥Using Hono is super easy. We can set up the project, write code, develop with a local server, and deploy quickly. The same code will work on any runtime, just with different entry points. Let's look at the basic usage of Hono.
## 入门
¥Starter
每个平台都有入门模板。使用以下 "create-hono" 命令。
¥Starter templates are available for each platform. Use the following "create-hono" command.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono@latest my-app
```
:::
然后会询问你要使用哪个模板。让我们为这个例子选择 Cloudflare Workers。
¥Then you will be asked which template you would like to use.
Let's select Cloudflare Workers for this example.
```
? Which template do you want to use?
aws-lambda
bun
cloudflare-pages
❯ cloudflare-workers
deno
fastly
nextjs
nodejs
vercel
```
模板将被拉入 `my-app`,因此请转到它并安装依赖。
¥The template will be pulled into `my-app`, so go to it and install the dependencies.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
软件包安装完成后,运行以下命令启动本地服务器。
¥Once the package installation is complete, run the following command to start up a local server.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
## Hello World
你可以使用 Cloudflare Workers 开发工具 "Wrangler"、Deno、Bun 或其他工具以 TypeScript 编写代码,而无需注意转译。
¥You can write code in TypeScript with the Cloudflare Workers development tool "Wrangler", Deno, Bun, or others without being aware of transpiling.
在 `src/index.ts` 中使用 Hono 编写你的第一个应用。以下示例是入门级 Hono 应用。
¥Write your first application with Hono in `src/index.ts`. The example below is a starter Hono application.
`import` 和最终的 `export default` 部分可能因运行时而异,但所有应用代码将在任何地方运行相同的代码。
¥The `import` and the final `export default` parts may vary from runtime to runtime,
but all of the application code will run the same code everywhere.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.text('Hello Hono!')
})
export default app
```
启动开发服务器并使用浏览器访问 `http://localhost:8787`。
¥Start the development server and access `http://localhost:8787` with your browser.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
## 返回 JSON
¥Return JSON
返回 JSON 也很容易。以下是处理对 `/api/hello` 的 GET 请求并返回 `application/json` 响应的示例。
¥Returning JSON is also easy. The following is an example of handling a GET Request to `/api/hello` and returning an `application/json` Response.
```ts
app.get('/api/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
ok: true,
message: 'Hello Hono!',
})
})
```
## 请求和响应
¥Request and Response
获取路径参数、URL 查询值并附加响应标头的写法如下。
¥Getting a path parameter, URL query value, and appending a Response header is written as follows.
```ts
app.get('/posts/:id', (c) => {
const page = c.req.query('page')
const id = c.req.param('id')
c.header('X-Message', 'Hi!')
return c.text(`You want to see ${page} of ${id}`)
})
```
我们可以轻松处理 POST、PUT 和 DELETE,而不仅仅是 GET。
¥We can easily handle POST, PUT, and DELETE not only GET.
```ts
app.post('/posts', (c) => c.text('Created!', 201))
app.delete('/posts/:id', (c) =>
c.text(`${c.req.param('id')} is deleted!`)
)
```
## 返回 HTML
¥Return HTML
你可以使用 [html 助手](/docs/helpers/html) 或 [JSX](/docs/guides/jsx) 语法编写 HTML。如果要使用 JSX,请将文件重命名为 `src/index.tsx` 并进行配置(请检查每个运行时,因为它们不同)。下面是使用 JSX 的示例。
¥You can write HTML with [the html Helper](/docs/helpers/html) or using [JSX](/docs/guides/jsx) syntax. If you want to use JSX, rename the file to `src/index.tsx` and configure it (check with each runtime as it is different). Below is an example using JSX.
```tsx
const View = () => {
return (
Hello Hono!
)
}
app.get('/page', (c) => {
return c.html()
})
```
## 返回原始响应
¥Return raw Response
你还可以返回原始 [响应](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/Response)。
¥You can also return the raw [Response](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/Response).
```ts
app.get('/', () => {
return new Response('Good morning!')
})
```
## 使用中间件
¥Using Middleware
中间件可以为你完成艰苦的工作。例如,添加基本身份验证。
¥Middleware can do the hard work for you.
For example, add in Basic Authentication.
```ts
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
// ...
app.use(
'/admin/*',
basicAuth({
username: 'admin',
password: 'secret',
})
)
app.get('/admin', (c) => {
return c.text('You are authorized!')
})
```
有有用的内置中间件,包括 Bearer 和使用 JWT、CORS 和 ETag 的身份验证。Hono 还使用外部库(如 GraphQL Server 和 Firebase Auth)提供第三方中间件。你可以制作自己的中间件。
¥There are useful built-in middleware including Bearer and authentication using JWT, CORS and ETag.
Hono also provides third-party middleware using external libraries such as GraphQL Server and Firebase Auth.
And, you can make your own middleware.
## 适配器
¥Adapter
有用于平台相关函数的适配器,例如处理静态文件或 WebSocket。例如,要在 Cloudflare Workers 中处理 WebSocket,请导入 `hono/cloudflare-workers`。
¥There are Adapters for platform-dependent functions, e.g., handling static files or WebSocket.
For example, to handle WebSocket in Cloudflare Workers, import `hono/cloudflare-workers`.
```ts
import { upgradeWebSocket } from 'hono/cloudflare-workers'
app.get(
'/ws',
upgradeWebSocket((c) => {
// ...
})
)
```
## 下一步
¥Next step
大多数代码可以在任何平台上运行,但每个平台都有指南。例如,如何设置项目或如何部署。请参阅你要用于创建应用的确切平台的页面!
¥Most code will work on any platform, but there are guides for each.
For instance, how to set up projects or how to deploy.
Please see the page for the exact platform you want to use to create your application!
# Bun
[Bun](https://bun.sh) 是另一个 JavaScript 运行时。它不是 Node.js 或 Deno。Bun 包含一个转译编译器,我们可以使用 TypeScript 编写代码。Hono 也适用于 Bun。
¥[Bun](https://bun.sh) is another JavaScript runtime. It's not Node.js or Deno. Bun includes a trans compiler, we can write the code with TypeScript.
Hono also works on Bun.
## 1. 安装 Bun
¥ Install Bun
要安装 `bun` 命令,请按照 [官方网站](https://bun.sh) 中的说明进行操作。
¥To install `bun` command, follow the instruction in [the official web site](https://bun.sh).
## 2. 设置
¥ Setup
### 2.1.设置新项目
¥2.1. Setup a new project
Bun 的入门程序可用。使用 "bun create" 命令启动你的项目。为此示例选择 `bun` 模板。
¥A starter for Bun is available. Start your project with "bun create" command.
Select `bun` template for this example.
```sh
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
移入 my-app 并安装依赖。
¥Move into my-app and install the dependencies.
```sh
cd my-app
bun install
```
### 2.2.设置现有项目
¥2.2. Setup an existing project
在现有的 Bun 项目中,我们只需要通过以下方式在项目根目录中安装 `hono` 依赖:
¥On an existing Bun project, we only need to install `hono` dependencies on the project root directory via
```sh
bun add hono
```
## 3. Hello World
"Hello World" 脚本如下。几乎与在其他平台上编写相同。
¥"Hello World" script is below. Almost the same as writing on other platforms.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Bun!'))
export default app
```
## 4. 运行
¥ Run
运行命令。
¥Run the command.
```sh
bun run dev
```
然后,在你的浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:3000`。
¥Then, access `http://localhost:3000` in your browser.
## 更改端口编号
¥Change port number
你可以通过导出 `port` 来指定端口号。
¥You can specify the port number with exporting the `port`.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Bun!'))
export default app // [!code --]
export default { // [!code ++]
port: 3000, // [!code ++]
fetch: app.fetch, // [!code ++]
} // [!code ++]
```
## 提供静态文件
¥Serve static files
要提供静态文件,请使用从 `hono/bun` 导入的 `serveStatic`。
¥To serve static files, use `serveStatic` imported from `hono/bun`.
```ts
import { serveStatic } from 'hono/bun'
const app = new Hono()
app.use('/static/*', serveStatic({ root: './' }))
app.use('/favicon.ico', serveStatic({ path: './favicon.ico' }))
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('You can access: /static/hello.txt'))
app.get('*', serveStatic({ path: './static/fallback.txt' }))
```
对于上述代码,它将与以下目录结构配合良好。
¥For the above code, it will work well with the following directory structure.
```
./
├── favicon.ico
├── src
└── static
├── demo
│ └── index.html
├── fallback.txt
├── hello.txt
└── images
└── dinotocat.png
```
### `rewriteRequestPath`
如果你想要将 `http://localhost:3000/static/*` 映射到 `./statics`,你可以使用 `rewriteRequestPath` 选项:
¥If you want to map `http://localhost:3000/static/*` to `./statics`, you can use the `rewriteRequestPath` option:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
root: './',
rewriteRequestPath: (path) =>
path.replace(/^\/static/, '/statics'),
})
)
```
### `mimes`
你可以使用 `mimes` 添加 MIME 类型:
¥You can add MIME types with `mimes`:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
mimes: {
m3u8: 'application/vnd.apple.mpegurl',
ts: 'video/mp2t',
},
})
)
```
### `onFound`
你可以使用 `onFound` 指定找到请求的文件时的处理:
¥You can specify handling when the requested file is found with `onFound`:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
// ...
onFound: (_path, c) => {
c.header('Cache-Control', `public, immutable, max-age=31536000`)
},
})
)
```
### `onNotFound`
你可以使用 `onNotFound` 指定未找到请求的文件时的处理:
¥You can specify handling when the requested file is not found with `onNotFound`:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
onNotFound: (path, c) => {
console.log(`${path} is not found, you access ${c.req.path}`)
},
})
)
```
### `precompressed`
`precompressed` 选项检查是否有扩展名为 `.br` 或 `.gz` 的文件,并根据 `Accept-Encoding` 标头提供这些文件。它优先考虑 Brotli,然后是 Zstd 和 Gzip。如果没有可用的目标,它将提供原始文件。
¥The `precompressed` option checks if files with extensions like `.br` or `.gz` are available and serves them based on the `Accept-Encoding` header. It prioritizes Brotli, then Zstd, and Gzip. If none are available, it serves the original file.
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
precompressed: true,
})
)
```
## 测试
¥Testing
你可以使用 `bun:test` 在 Bun 上进行测试。
¥You can use `bun:test` for testing on Bun.
```ts
import { describe, expect, it } from 'bun:test'
import app from '.'
describe('My first test', () => {
it('Should return 200 Response', async () => {
const req = new Request('http://localhost/')
const res = await app.fetch(req)
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
})
})
```
然后,运行命令。
¥Then, run the command.
```sh
bun test index.test.ts
```
# Cloudflare 页面
¥Cloudflare Pages
[Cloudflare 页面](https://pages.cloudflare.com) 是全栈 Web 应用的边缘平台。它提供由 Cloudflare Workers 提供的静态文件和动态内容。
¥[Cloudflare Pages](https://pages.cloudflare.com) is an edge platform for full-stack web applications.
It serves static files and dynamic content provided by Cloudflare Workers.
Hono 完全支持 Cloudflare Pages。它带来了令人愉悦的开发者体验。Vite 的开发服务器速度很快,使用 Wrangler 部署速度超快。
¥Hono fully supports Cloudflare Pages.
It introduces a delightful developer experience. Vite's dev server is fast, and deploying with Wrangler is super quick.
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
Cloudflare Pages 的入门程序可用。使用 "create-hono" 命令启动你的项目。为此示例选择 `cloudflare-pages` 模板。
¥A starter for Cloudflare Pages is available.
Start your project with "create-hono" command.
Select `cloudflare-pages` template for this example.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
移入 `my-app` 并安装依赖。
¥Move into `my-app` and install the dependencies.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
下面是一个基本的目录结构。
¥Below is a basic directory structure.
```text
./
├── package.json
├── public
│ └── static // Put your static files.
│ └── style.css // You can refer to it as `/static/style.css`.
├── src
│ ├── index.tsx // The entry point for server-side.
│ └── renderer.tsx
├── tsconfig.json
└── vite.config.ts
```
## 2. Hello World
按如下方式编辑 `src/index.tsx`:
¥Edit `src/index.tsx` like the following:
```tsx
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { renderer } from './renderer'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('*', renderer)
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.render(
Hello, Cloudflare Pages!
)
})
export default app
```
## 3. 运行
¥ Run
在本地运行开发服务器。然后,在你的 Web 浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:5173`。
¥Run the development server locally. Then, access `http://localhost:5173` in your Web browser.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
## 4. 部署
¥ Deploy
如果你有 Cloudflare 账户,可以部署到 Cloudflare。在 `package.json` 中,需要将 `$npm_execpath` 更改为你选择的包管理器。
¥If you have a Cloudflare account, you can deploy to Cloudflare. In `package.json`, `$npm_execpath` needs to be changed to your package manager of choice.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run deploy
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn deploy
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm run deploy
```
```sh [bun]
bun run deploy
```
:::
### 通过 Cloudflare 仪表板使用 GitHub 部署
¥Deploy via the Cloudflare dashboard with GitHub
1. 登录 [Cloudflare 仪表板](https://dash.cloudflare.com) 并选择你的账户。
¥Log in to the [Cloudflare dashboard](https://dash.cloudflare.com) and select your account.
2. 在 Account Home 中,选择 Workers & Pages > Create application > Pages > Connect to Git。
¥In Account Home, select Workers & Pages > Create application > Pages > Connect to Git.
3. 授权你的 GitHub 账户,然后选择存储库。在设置构建和部署中,提供以下信息:
¥Authorize your GitHub account, and select the repository. In Set up builds and deployments, provide the following information:
| 配置选项 | 值 |
| ---- | --------------- |
| 生产分支 | `main` |
| 构建命令 | `npm run build` |
| 构建目录 | `dist` |
## 绑定
¥Bindings
你可以使用 Cloudflare 绑定,如变量、KV、D1 等。在本节中,让我们使用变量和 KV。
¥You can use Cloudflare Bindings like Variables, KV, D1, and others.
In this section, let's use Variables and KV.
### 创建 `wrangler.toml`
¥Create `wrangler.toml`
首先,为本地绑定创建 `wrangler.toml`:
¥First, create `wrangler.toml` for local Bindings:
```sh
touch wrangler.toml
```
编辑 `wrangler.toml`。使用名称 `MY_NAME` 指定变量。
¥Edit `wrangler.toml`. Specify Variable with the name `MY_NAME`.
```toml
[vars]
MY_NAME = "Hono"
```
### 创建 KV
¥Create KV
接下来,制作 KV。运行以下 `wrangler` 命令:
¥Next, make the KV. Run the following `wrangler` command:
```sh
wrangler kv namespace create MY_KV --preview
```
记下 `preview_id` 作为以下输出:
¥Note down the `preview_id` as the following output:
```
{ binding = "MY_KV", preview_id = "abcdef" }
```
使用 Bindings、`MY_KV` 的名称指定 `preview_id`:
¥Specify `preview_id` with the name of Bindings, `MY_KV`:
```toml
[[kv_namespaces]]
binding = "MY_KV"
id = "abcdef"
```
### 编辑 `vite.config.ts`
¥Edit `vite.config.ts`
编辑 `vite.config.ts`:
¥Edit the `vite.config.ts`:
```ts
import devServer from '@hono/vite-dev-server'
import adapter from '@hono/vite-dev-server/cloudflare'
import build from '@hono/vite-cloudflare-pages'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
devServer({
entry: 'src/index.tsx',
adapter, // Cloudflare Adapter
}),
build(),
],
})
```
### 在你的应用中使用绑定
¥Use Bindings in your application
在你的应用中使用 Variable 和 KV。设置类型。
¥Use Variable and KV in your application. Set the types.
```ts
type Bindings = {
MY_NAME: string
MY_KV: KVNamespace
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
```
使用它们:
¥Use them:
```tsx
app.get('/', async (c) => {
await c.env.MY_KV.put('name', c.env.MY_NAME)
const name = await c.env.MY_KV.get('name')
return c.render(
Hello! {name}
)
})
```
### 在生产中
¥In production
对于 Cloudflare Pages,你将使用 `wrangler.toml` 进行本地开发,但对于生产,你将在仪表板中设置绑定。
¥For Cloudflare Pages, you will use `wrangler.toml` for local development, but for production, you will set up Bindings in the dashboard.
## 客户端
¥Client-side
你可以编写客户端脚本并使用 Vite 的功能将其导入你的应用。如果 `/src/client.ts` 是客户端的入口点,只需将其写入脚本标记中即可。此外,`import.meta.env.PROD` 对于检测它是在开发服务器上运行还是在构建阶段运行很有用。
¥You can write client-side scripts and import them into your application using Vite's features.
If `/src/client.ts` is the entry point for the client, simply write it in the script tag.
Additionally, `import.meta.env.PROD` is useful for detecting whether it's running on a dev server or in the build phase.
```tsx
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html(
{import.meta.env.PROD ? (
) : (
)}
Hello
)
})
```
为了正确构建脚本,你可以使用示例配置文件 `vite.config.ts`,如下所示。
¥In order to build the script properly, you can use the example config file `vite.config.ts` as shown below.
```ts
import pages from '@hono/vite-cloudflare-pages'
import devServer from '@hono/vite-dev-server'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
export default defineConfig(({ mode }) => {
if (mode === 'client') {
return {
build: {
rollupOptions: {
input: './src/client.ts',
output: {
entryFileNames: 'static/client.js',
},
},
},
}
} else {
return {
plugins: [
pages(),
devServer({
entry: 'src/index.tsx',
}),
],
}
}
})
```
你可以运行以下命令来构建服务器和客户端脚本。
¥You can run the following command to build the server and client script.
```sh
vite build --mode client && vite build
```
## Cloudflare 页面中间件
¥Cloudflare Pages Middleware
Cloudflare Pages 使用自己的 [中间件](https://developers.cloudflare.com/pages/functions/middleware/) 系统,与 Hono 的中间件不同。你可以通过将 `onRequest` 导出到名为 `_middleware.ts` 的文件中来启用它,如下所示:
¥Cloudflare Pages uses its own [middleware](https://developers.cloudflare.com/pages/functions/middleware/) system that is different from Hono's middleware. You can enable it by exporting `onRequest` in a file named `_middleware.ts` like this:
```ts
// functions/_middleware.ts
export async function onRequest(pagesContext) {
console.log(`You are accessing ${pagesContext.request.url}`)
return await pagesContext.next()
}
```
使用 `handleMiddleware`,你可以将 Hono 的中间件用作 Cloudflare Pages 中间件。
¥Using `handleMiddleware`, you can use Hono's middleware as Cloudflare Pages middleware.
```ts
// functions/_middleware.ts
import { handleMiddleware } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
export const onRequest = handleMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
console.log(`You are accessing ${c.req.url}`)
await next()
})
```
你还可以为 Hono 使用内置和第三方中间件。例如,要添加基本身份验证,你可以使用 [Hono 的基本身份验证中间件](/docs/middleware/builtin/basic-auth)。
¥You can also use built-in and 3rd party middleware for Hono. For example, to add Basic Authentication, you can use [Hono's Basic Authentication Middleware](/docs/middleware/builtin/basic-auth).
```ts
// functions/_middleware.ts
import { handleMiddleware } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
export const onRequest = handleMiddleware(
basicAuth({
username: 'hono',
password: 'acoolproject',
})
)
```
如果要应用多个中间件,可以这样写:
¥If you want to apply multiple middleware, you can write it like this:
```ts
import { handleMiddleware } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
// ...
export const onRequest = [
handleMiddleware(middleware1),
handleMiddleware(middleware2),
handleMiddleware(middleware3),
]
```
### 访问 `EventContext`
¥Accessing `EventContext`
你可以通过 `handleMiddleware` 中的 `c.env` 访问 [`EventContext`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/pages/functions/api-reference/#eventcontext) 对象。
¥You can access [`EventContext`](https://developers.cloudflare.com/pages/functions/api-reference/#eventcontext) object via `c.env` in `handleMiddleware`.
```ts
// functions/_middleware.ts
import { handleMiddleware } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
export const onRequest = [
handleMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
c.env.eventContext.data.user = 'Joe'
await next()
}),
]
```
然后,你可以通过处理程序中的 `c.env.eventContext` 访问数据值:
¥Then, you can access the data value in via `c.env.eventContext` in the handler:
```ts
// functions/api/[[route]].ts
import type { EventContext } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
import { handle } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
// ...
type Env = {
Bindings: {
eventContext: EventContext
}
}
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: `Hello, ${c.env.eventContext.data.user}!`, // 'Joe'
})
})
export const onRequest = handle(app)
```
# Cloudflare Workers
[Cloudflare Workers](https://workers.cloudflare.com) 是 Cloudflare CDN 上的 JavaScript 边缘运行时。
¥[Cloudflare Workers](https://workers.cloudflare.com) is a JavaScript edge runtime on Cloudflare CDN.
你可以在本地开发应用并使用 [Wrangler](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/) 使用几个命令发布它。Wrangler 包含 trans 编译器,因此我们可以使用 TypeScript 编写代码。
¥You can develop the application locally and publish it with a few commands using [Wrangler](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/).
Wrangler includes trans compiler, so we can write the code with TypeScript.
让我们用 Hono 为 Cloudflare Workers 制作你的第一个应用。
¥Let’s make your first application for Cloudflare Workers with Hono.
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
Cloudflare Workers 的入门程序可用。使用 "create-hono" 命令启动你的项目。为此示例选择 `cloudflare-workers` 模板。
¥A starter for Cloudflare Workers is available.
Start your project with "create-hono" command.
Select `cloudflare-workers` template for this example.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
移至 `my-app` 并安装依赖。
¥Move to `my-app` and install the dependencies.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
按如下方式编辑 `src/index.ts`。
¥Edit `src/index.ts` like below.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Cloudflare Workers!'))
export default app
```
## 3. 运行
¥ Run
在本地运行开发服务器。然后,在你的 Web 浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:8787`。
¥Run the development server locally. Then, access `http://localhost:8787` in your web browser.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
### 更改端口编号
¥Change port number
如果你需要更改端口号,可以按照此处的说明更新 `wrangler.toml` / `wrangler.json` / `wrangler.jsonc` 文件:[Wrangler 配置](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/#local-development-settings)
¥If you need to change the port number you can follow the instructions here to update `wrangler.toml` / `wrangler.json` / `wrangler.jsonc` files:
[Wrangler Configuration](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/#local-development-settings)
或者,你可以按照此处的说明设置 CLI 选项:[Wrangler CLI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/commands/#dev)
¥Or, you can follow the instructions here to set CLI options:
[Wrangler CLI](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/commands/#dev)
## 4. 部署
¥ Deploy
如果你有 Cloudflare 账户,可以部署到 Cloudflare。在 `package.json` 中,需要将 `$npm_execpath` 更改为你选择的包管理器。
¥If you have a Cloudflare account, you can deploy to Cloudflare. In `package.json`, `$npm_execpath` needs to be changed to your package manager of choice.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run deploy
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn deploy
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm run deploy
```
```sh [bun]
bun run deploy
```
:::
就这些!
¥That's all!
## 服务工作线程模式或模块工作线程模式
¥Service Worker mode or Module Worker mode
有两种用于编写 Cloudflare Workers 的语法。Module Worker 模式和 Service Worker 模式。使用 Hono,你可以同时使用两种语法编写,但我们建议使用 Module Worker 模式,以便绑定变量本地化。
¥There are two syntaxes for writing the Cloudflare Workers. *Module Worker mode* and *Service Worker mode*. Using Hono, you can write with both syntax, but we recommend using Module Worker mode so that binding variables are localized.
```ts
// Module Worker
export default app
```
```ts
// Service Worker
app.fire()
```
## 将 Hono 与其他事件处理程序一起使用
¥Using Hono with other event handlers
你可以在 Module Worker 模式下将 Hono 与其他事件处理程序(例如 `scheduled`)集成。
¥You can integrate Hono with other event handlers (such as `scheduled`) in *Module Worker mode*.
为此,请将 `app.fetch` 导出为模块的 `fetch` 处理程序,然后根据需要实现其他处理程序:
¥To do this, export `app.fetch` as the module's `fetch` handler, and then implement other handlers as needed:
```ts
const app = new Hono()
export default {
fetch: app.fetch,
scheduled: async (batch, env) => {},
}
```
## 提供静态文件
¥Serve static files
如果你想要提供静态文件,你可以使用 Cloudflare Workers 的 [静态资源功能](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/static-assets/)。指定 `wrangler.toml` 中文件的目录:
¥If you want to serve static files, you can use [the Static Assets feature](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/static-assets/) of Cloudflare Workers. Specify the directory for the files in `wrangler.toml`:
```toml
assets = { directory = "public" }
```
然后创建 `public` 目录并将文件放在那里。例如,`./public/static/hello.txt` 将作为 `/static/hello.txt` 提供。
¥Then create the `public` directory and place the files there. For instance, `./public/static/hello.txt` will be served as `/static/hello.txt`.
```
.
├── package.json
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico
│ └── static
│ └── hello.txt
├── src
│ └── index.ts
└── wrangler.toml
```
## 类型
¥Types
如果你想拥有 worker 类型,则必须安装 `@cloudflare/workers-types`。
¥You have to install `@cloudflare/workers-types` if you want to have workers types.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i --save-dev @cloudflare/workers-types
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add -D @cloudflare/workers-types
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add -D @cloudflare/workers-types
```
```sh [bun]
bun add --dev @cloudflare/workers-types
```
:::
## 测试
¥Testing
对于测试,我们建议使用 `@cloudflare/vitest-pool-workers`。请参阅 [examples](https://github.com/honojs/examples) 进行设置。
¥For testing, we recommend using `@cloudflare/vitest-pool-workers`.
Refer to [examples](https://github.com/honojs/examples) for setting it up.
如果有以下应用。
¥If there is the application below.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Please test me!'))
```
我们可以使用此代码测试它是否返回 "200 OK" 响应。
¥We can test if it returns "*200 OK*" Response with this code.
```ts
describe('Test the application', () => {
it('Should return 200 response', async () => {
const res = await app.request('http://localhost/')
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
})
})
```
## 绑定
¥Bindings
在 Cloudflare Workers 中,我们可以绑定环境值、KV 命名空间、R2 bucket 或 Durable Object。你可以在 `c.env` 中访问它们。如果你将绑定的 "类型结构" 作为泛型传递给 `Hono`,它将具有类型。
¥In the Cloudflare Workers, we can bind the environment values, KV namespace, R2 bucket, or Durable Object. You can access them in `c.env`. It will have the types if you pass the "*type struct*" for the bindings to the `Hono` as generics.
```ts
type Bindings = {
MY_BUCKET: R2Bucket
USERNAME: string
PASSWORD: string
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
// Access to environment values
app.put('/upload/:key', async (c, next) => {
const key = c.req.param('key')
await c.env.MY_BUCKET.put(key, c.req.body)
return c.text(`Put ${key} successfully!`)
})
```
## 在中间件中使用变量
¥Using Variables in Middleware
这是 Module Worker 模式的唯一情况。如果要在中间件中使用变量或秘密变量,例如基本身份验证中间件中的 "username" 或 "password",则需要像下面这样编写。
¥This is the only case for Module Worker mode.
If you want to use Variables or Secret Variables in Middleware, for example, "username" or "password" in Basic Authentication Middleware, you need to write like the following.
```ts
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
type Bindings = {
USERNAME: string
PASSWORD: string
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
//...
app.use('/auth/*', async (c, next) => {
const auth = basicAuth({
username: c.env.USERNAME,
password: c.env.PASSWORD,
})
return auth(c, next)
})
```
同样适用于 Bearer 身份验证中间件、JWT 身份验证或其他。
¥The same is applied to Bearer Authentication Middleware, JWT Authentication, or others.
## 从 GitHub Actions 部署
¥Deploy from GitHub Actions
在通过 CI 将代码部署到 Cloudflare 之前,你需要一个 Cloudflare 令牌。你可以从 [用户 API 令牌](https://dash.cloudflare.com/profile/api-tokens) 进行管理。
¥Before deploying code to Cloudflare via CI, you need a Cloudflare token. You can manage it from [User API Tokens](https://dash.cloudflare.com/profile/api-tokens).
如果是新创建的令牌,请选择编辑 Cloudflare Workers 模板,如果你已经有另一个令牌,请确保该令牌具有相应的权限(否,令牌权限不在 Cloudflare Pages 和 Cloudflare Workers 之间共享)。
¥If it's a newly created token, select the **Edit Cloudflare Workers** template, if you already have another token, make sure the token has the corresponding permissions(No, token permissions are not shared between Cloudflare Pages and Cloudflare Workers).
然后转到你的 GitHub 存储库设置仪表板:`Settings->Secrets and variables->Actions->Repository secrets`,并添加一个名为 `CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN` 的新密钥。
¥then go to your GitHub repository settings dashboard: `Settings->Secrets and variables->Actions->Repository secrets`, and add a new secret with the name `CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN`.
然后在你的 Hono 项目根文件夹中创建 `.github/workflows/deploy.yml`,粘贴以下代码:
¥then create `.github/workflows/deploy.yml` in your Hono project root folder, paste the following code:
```yml
name: Deploy
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Deploy
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Deploy
uses: cloudflare/wrangler-action@v3
with:
apiToken: ${{ secrets.CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN }}
```
然后编辑 `wrangler.toml`,并在 `compatibility_date` 行后添加此代码。
¥then edit `wrangler.toml`, and add this code after `compatibility_date` line.
```toml
main = "src/index.ts"
minify = true
```
一切就绪!现在推送代码并享受它。
¥Everything is ready! Now push the code and enjoy it.
## 本地开发时加载环境
¥Load env when local development
要配置本地开发的环境变量,请在项目根目录中创建 `.dev.vars` 文件。然后像使用普通环境文件一样配置环境变量。
¥To configure the environment variables for local development, create the `.dev.vars` file in the root directory of the project.
Then configure your environment variables as you would with a normal env file.
```
SECRET_KEY=value
API_TOKEN=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9
```
> 有关此部分的更多信息,你可以在 Cloudflare 文档中找到:[https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/#secrets](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/#secrets)
>
> ¥For more about this section you can find in the Cloudflare documentation:
> [https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/#secrets](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/wrangler/configuration/#secrets)
然后我们使用 `c.env.*` 获取代码中的环境变量。对于 Cloudflare Workers,必须通过 `c` 获取环境变量,而不是通过 `process.env`。
¥Then we use the `c.env.*` to get the environment variables in our code.\
**For Cloudflare Workers, environment variables must be obtained via `c`, not via `process.env`.**
```ts
type Bindings = {
SECRET_KEY: string
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get('/env', (c) => {
const SECRET_KEY = c.env.SECRET_KEY
return c.text(SECRET_KEY)
})
```
在将项目部署到 Cloudflare 之前,请记住在 Cloudflare Workers 项目的配置中设置环境变量/密钥。
¥Before you deploy your project to Cloudflare, remember to set the environment variable/secrets in the Cloudflare Workers project's configuration.
> 有关此部分的更多信息,你可以在 Cloudflare 文档中找到:[https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/configuration/environment-variables/#add-environment-variables-via-the-dashboard](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/configuration/environment-variables/#add-environment-variables-via-the-dashboard)
>
> ¥For more about this section you can find in the Cloudflare documentation:
> [https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/configuration/environment-variables/#add-environment-variables-via-the-dashboard](https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/configuration/environment-variables/#add-environment-variables-via-the-dashboard)
# Deno
[Deno](https://deno.com/) 是基于 V8 构建的 JavaScript 运行时。它不是 Node.js。Hono 也适用于 Deno。
¥[Deno](https://deno.com/) is a JavaScript runtime built on V8. It's not Node.js.
Hono also works on Deno.
你可以使用 Hono,用 TypeScript 编写代码,使用 `deno` 命令运行应用,然后将其部署到 "Deno 部署"。
¥You can use Hono, write the code with TypeScript, run the application with the `deno` command, and deploy it to "Deno Deploy".
## 1. 安装 Deno
¥ Install Deno
首先,安装 `deno` 命令。请参考 [官方文档](https://docs.deno.com/runtime/manual/getting_started/installation)。
¥First, install `deno` command.
Please refer to [the official document](https://docs.deno.com/runtime/manual/getting_started/installation).
## 2. 设置
¥ Setup
Deno 的启动器可用。使用 "create-hono" 命令启动你的项目。
¥A starter for Deno is available.
Start your project with "create-hono" command.
```sh
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
为此示例选择 `deno` 模板。
¥Select `deno` template for this example.
移入 `my-app`。对于 Deno,你不必明确安装 Hono。
¥Move into `my-app`. For Deno, you don't have to install Hono explicitly.
```sh
cd my-app
```
## 3. Hello World
编写你的第一个应用。
¥Write your first application.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Deno!'))
Deno.serve(app.fetch)
```
## 4. 运行
¥ Run
只需这个命令:
¥Just this command:
```sh
deno task start
```
## 更改端口编号
¥Change port number
你可以通过在 `main.ts` 中更新 `Deno.serve` 的参数来指定端口号:
¥You can specify the port number by updating the arguments of `Deno.serve` in `main.ts`:
```ts
Deno.serve(app.fetch) // [!code --]
Deno.serve({ port: 8787 }, app.fetch) // [!code ++]
```
## 提供静态文件
¥Serve static files
要提供静态文件,请使用从 `hono/middleware.ts` 导入的 `serveStatic`。
¥To serve static files, use `serveStatic` imported from `hono/middleware.ts`.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { serveStatic } from 'hono/deno'
const app = new Hono()
app.use('/static/*', serveStatic({ root: './' }))
app.use('/favicon.ico', serveStatic({ path: './favicon.ico' }))
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('You can access: /static/hello.txt'))
app.get('*', serveStatic({ path: './static/fallback.txt' }))
Deno.serve(app.fetch)
```
对于上述代码,它将与以下目录结构配合良好。
¥For the above code, it will work well with the following directory structure.
```
./
├── favicon.ico
├── index.ts
└── static
├── demo
│ └── index.html
├── fallback.txt
├── hello.txt
└── images
└── dinotocat.png
```
### `rewriteRequestPath`
如果你想要将 `http://localhost:8000/static/*` 映射到 `./statics`,你可以使用 `rewriteRequestPath` 选项:
¥If you want to map `http://localhost:8000/static/*` to `./statics`, you can use the `rewriteRequestPath` option:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
root: './',
rewriteRequestPath: (path) =>
path.replace(/^\/static/, '/statics'),
})
)
```
### `mimes`
你可以使用 `mimes` 添加 MIME 类型:
¥You can add MIME types with `mimes`:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
mimes: {
m3u8: 'application/vnd.apple.mpegurl',
ts: 'video/mp2t',
},
})
)
```
### `onFound`
你可以使用 `onFound` 指定找到请求的文件时的处理:
¥You can specify handling when the requested file is found with `onFound`:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
// ...
onFound: (_path, c) => {
c.header('Cache-Control', `public, immutable, max-age=31536000`)
},
})
)
```
### `onNotFound`
你可以使用 `onNotFound` 指定未找到请求的文件时的处理:
¥You can specify handling when the requested file is not found with `onNotFound`:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
onNotFound: (path, c) => {
console.log(`${path} is not found, you access ${c.req.path}`)
},
})
)
```
### `precompressed`
`precompressed` 选项检查是否有扩展名为 `.br` 或 `.gz` 的文件,并根据 `Accept-Encoding` 标头提供这些文件。它优先考虑 Brotli,然后是 Zstd 和 Gzip。如果没有可用的目标,它将提供原始文件。
¥The `precompressed` option checks if files with extensions like `.br` or `.gz` are available and serves them based on the `Accept-Encoding` header. It prioritizes Brotli, then Zstd, and Gzip. If none are available, it serves the original file.
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
precompressed: true,
})
)
```
## Deno 部署
¥Deno Deploy
Deno Deploy 是 Deno 的边缘运行时平台。我们可以在 Deno Deploy 上向全世界发布应用。
¥Deno Deploy is an edge runtime platform for Deno.
We can publish the application world widely on Deno Deploy.
Hono 还支持 Deno Deploy。请参考 [官方文档](https://docs.deno.com/deploy/manual/)。
¥Hono also supports Deno Deploy. Please refer to [the official document](https://docs.deno.com/deploy/manual/).
## 测试
¥Testing
在 Deno 上测试应用很容易。你可以使用 `Deno.test` 编写并使用 `assert` 或 `assertEquals`(从 [@std/assert](https://jsr.io/@std/assert) 开始)。
¥Testing the application on Deno is easy.
You can write with `Deno.test` and use `assert` or `assertEquals` from [@std/assert](https://jsr.io/@std/assert).
```sh
deno add jsr:@std/assert
```
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { assertEquals } from '@std/assert'
Deno.test('Hello World', async () => {
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Please test me'))
const res = await app.request('http://localhost/')
assertEquals(res.status, 200)
})
```
然后运行命令:
¥Then run the command:
```sh
deno test hello.ts
```
## `npm:` 说明符
¥`npm:` specifier
`npm:hono` 也可用。你可以通过修复 `deno.json` 来使用它:
¥`npm:hono` is also available. You can use it by fixing the `deno.json`:
```json
{
"imports": {
"hono": "jsr:@hono/hono" // [!code --]
"hono": "npm:hono" // [!code ++]
}
}
```
你可以使用 `npm:hono` 或 `jsr:@hono/hono`。
¥You can use either `npm:hono` or `jsr:@hono/hono`.
如果要将第三方中间件(如 `npm:@hono/zod-validator`)与 TypeScript 类型推断一起使用,则需要使用 `npm:` 说明符。
¥If you want to use Third-party Middleware such as `npm:@hono/zod-validator` with the TypeScript Type inferences, you need to use the `npm:` specifier.
```json
{
"imports": {
"hono": "npm:hono",
"zod": "npm:zod",
"@hono/zod-validator": "npm:@hono/zod-validator"
}
}
```
# Fastly 计算
¥Fastly Compute
[Fastly 的计算](https://www.fastly.com/products/edge-compute) 产品允许我们构建高规模、全球分布的应用并在 Fastly CDN 边缘执行代码。
¥[Fastly's Compute](https://www.fastly.com/products/edge-compute) offering allows us to build high scale, globally distributed applications and execute code at the edge of Fastly CDN.
Hono 也适用于 Fastly Compute。
¥Hono also works on Fastly Compute.
## 1. 安装 CLI
¥ Install CLI
要使用 Fastly Compute,如果你还没有 [创建一个 Fastly 账户](https://www.fastly.com/signup/),则必须有 [创建一个 Fastly 账户](https://www.fastly.com/signup/)。然后,安装 [Fastly CLI](https://github.com/fastly/cli)。
¥To use Fastly Compute, you must [create a Fastly account](https://www.fastly.com/signup/) if you don't already have one.
Then, install [Fastly CLI](https://github.com/fastly/cli).
macOS
```sh
brew install fastly/tap/fastly
```
其他操作系统请点击此链接:
¥Follow this link for other OS:
* [计算服务 | Fastly 开发者中心](https://developer.fastly.com/learning/compute/#download-and-install-the-fastly-cli)
¥[Compute services | Fastly Developer Hub](https://developer.fastly.com/learning/compute/#download-and-install-the-fastly-cli)
## 2. 设置
¥ Setup
Fastly Compute 的启动器可用。使用 "create-hono" 命令启动你的项目。为此示例选择 `fastly` 模板。
¥A starter for Fastly Compute is available.
Start your project with "create-hono" command.
Select `fastly` template for this example.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
移至 `my-app` 并安装依赖。
¥Move to `my-app` and install the dependencies.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
## 3. Hello World
编辑 `src/index.ts`:
¥Edit `src/index.ts`:
```ts
// src/index.ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Fastly!'))
app.fire()
```
## 4. 运行
¥ Run
在本地运行开发服务器。然后,在你的 Web 浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:7676`。
¥Run the development server locally. Then, access `http://localhost:7676` in your Web browser.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
## 4. 部署
¥ Deploy
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run deploy
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn deploy
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm deploy
```
```sh [bun]
bun run deploy
```
:::
就这些!!
¥That's all!!
# Lambda\@Edge
[Lambda@Edge](https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/edge/) 是 Amazon Web Services 的无服务器平台。它允许你在 Amazon CloudFront 的边缘位置运行 Lambda 函数,使你能够自定义 HTTP 请求/响应的行为。
¥[Lambda@Edge](https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/edge/) is a serverless platform by Amazon Web Services. It allows you to run Lambda functions at Amazon CloudFront's edge locations, enabling you to customize behaviors for HTTP requests/responses.
Hono 在 Node.js 18+ 环境中支持 Lambda@Edge。
¥Hono supports Lambda@Edge with the Node.js 18+ environment.
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
在 Lambda@Edge 上创建应用时,[CDK](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/serverless-cdk.html) 可用于设置 CloudFront、IAM 角色、API 网关等功能。
¥When creating the application on Lambda@Edge,
[CDK](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/serverless-cdk.html)
is useful to setup the functions such as CloudFront, IAM Role, API Gateway, and others.
使用 `cdk` CLI 初始化你的项目。
¥Initialize your project with the `cdk` CLI.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
npm i hono
mkdir lambda
```
```sh [yarn]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
yarn add hono
mkdir lambda
```
```sh [pnpm]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
pnpm add hono
mkdir lambda
```
```sh [bun]
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
cdk init app -l typescript
bun add hono
mkdir lambda
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `lambda/index_edge.ts`。
¥Edit `lambda/index_edge.ts`.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/lambda-edge'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Hono on Lambda@Edge!'))
export const handler = handle(app)
```
## 3. 部署
¥ Deploy
编辑 `bin/my-app.ts`。
¥Edit `bin/my-app.ts`.
```ts
#!/usr/bin/env node
import 'source-map-support/register'
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'
import { MyAppStack } from '../lib/my-app-stack'
const app = new cdk.App()
new MyAppStack(app, 'MyAppStack', {
env: {
account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT,
region: 'us-east-1',
},
})
```
编辑 `lambda/cdk-stack.ts`。
¥Edit `lambda/cdk-stack.ts`.
```ts
import { Construct } from 'constructs'
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib'
import * as cloudfront from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront'
import * as origins from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront-origins'
import * as lambda from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda'
import { NodejsFunction } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda-nodejs'
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3'
export class MyAppStack extends cdk.Stack {
public readonly edgeFn: lambda.Function
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props)
const edgeFn = new NodejsFunction(this, 'edgeViewer', {
entry: 'lambda/index_edge.ts',
handler: 'handler',
runtime: lambda.Runtime.NODEJS_20_X,
})
// Upload any html
const originBucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'originBucket')
new cloudfront.Distribution(this, 'Cdn', {
defaultBehavior: {
origin: new origins.S3Origin(originBucket),
edgeLambdas: [
{
functionVersion: edgeFn.currentVersion,
eventType: cloudfront.LambdaEdgeEventType.VIEWER_REQUEST,
},
],
},
})
}
}
```
最后,运行命令进行部署:
¥Finally, run the command to deploy:
```sh
cdk deploy
```
## 回调
¥Callback
如果要添加 Basic Auth 并在验证后继续处理请求,则可以使用 `c.env.callback()`
¥If you want to add Basic Auth and continue with request processing after verification, you can use `c.env.callback()`
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basic-auth'
import type { Callback, CloudFrontRequest } from 'hono/lambda-edge'
import { handle } from 'hono/lambda-edge'
type Bindings = {
callback: Callback
request: CloudFrontRequest
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get(
'*',
basicAuth({
username: 'hono',
password: 'acoolproject',
})
)
app.get('/', async (c, next) => {
await next()
c.env.callback(null, c.env.request)
})
export const handler = handle(app)
```
# Netlify
Netlify 提供静态站点托管和无服务器后端服务。[边缘函数](https://docs.netlify.com/edge-functions/overview/) 使我们能够使网页动态化。
¥Netlify provides static site hosting and serverless backend services. [Edge Functions](https://docs.netlify.com/edge-functions/overview/) enables us to make the web pages dynamic.
Edge Functions 支持用 Deno 和 TypeScript 编写,通过 [Netlify CLI](https://docs.netlify.com/cli/get-started/) 可以轻松部署。使用 Hono,你可以为 Netlify Edge Functions 创建应用。
¥Edge Functions support writing in Deno and TypeScript, and deployment is made easy through the [Netlify CLI](https://docs.netlify.com/cli/get-started/). With Hono, you can create the application for Netlify Edge Functions.
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
Netlify 的启动器可用。使用 "create-hono" 命令启动你的项目。为此示例选择 `netlify` 模板。
¥A starter for Netlify is available.
Start your project with "create-hono" command.
Select `netlify` template for this example.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
移入 `my-app`。
¥Move into `my-app`.
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `netlify/edge-functions/index.ts`:
¥Edit `netlify/edge-functions/index.ts`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'jsr:@hono/hono'
import { handle } from 'jsr:@hono/hono/netlify'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.text('Hello Hono!')
})
export default handle(app)
```
## 3. 运行
¥ Run
使用 Netlify CLI 运行开发服务器。然后,在你的 Web 浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:8888`。
¥Run the development server with Netlify CLI. Then, access `http://localhost:8888` in your Web browser.
```sh
netlify dev
```
## 4. 部署
¥ Deploy
你可以使用 `netlify deploy` 命令进行部署。
¥You can deploy with a `netlify deploy` command.
```sh
netlify deploy --prod
```
## `Context`
你可以通过 `c.env` 访问 Netlify 的 `Context`:
¥You can access the Netlify's `Context` through `c.env`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'jsr:@hono/hono'
import { handle } from 'jsr:@hono/hono/netlify'
// Import the type definition
import type { Context } from 'https://edge.netlify.com/'
export type Env = {
Bindings: {
context: Context
}
}
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/country', (c) =>
c.json({
'You are in': c.env.context.geo.country?.name,
})
)
export default handle(app)
```
# Node.js
[Node.js](https://nodejs.cn/) 是一个开源的跨平台 JavaScript 运行时环境。
¥[Node.js](https://nodejs.cn/) is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment.
Hono 最初并不是为 Node.js 设计的。但使用 [Node.js 适配器](https://github.com/honojs/node-server) 它也可以在 Node.js 上运行。
¥Hono was not designed for Node.js at first. But with a [Node.js Adapter](https://github.com/honojs/node-server) it can run on Node.js as well.
::: info 信息
它适用于大于 18.x 的 Node.js 版本。具体所需的 Node.js 版本如下:
¥It works on Node.js versions greater than 18.x. The specific required Node.js versions are as follows:
* 18.x => 18.14.1+
* 19.x => 19.7.0+
* 20.x => 20.0.0+
本质上,你可以简单地使用每个主要版本的最新版本。
¥Essentially, you can simply use the latest version of each major release.
:::
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
Node.js 的启动器可用。使用 "create-hono" 命令启动你的项目。为此示例选择 `nodejs` 模板。
¥A starter for Node.js is available.
Start your project with "create-hono" command.
Select `nodejs` template for this example.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
移至 `my-app` 并安装依赖。
¥Move to `my-app` and install the dependencies.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `src/index.ts`:
¥Edit `src/index.ts`:
```ts
import { serve } from '@hono/node-server'
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello Node.js!'))
serve(app)
```
## 3. 运行
¥ Run
在本地运行开发服务器。然后,在你的 Web 浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:3000`。
¥Run the development server locally. Then, access `http://localhost:3000` in your Web browser.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
:::
## 更改端口编号
¥Change port number
你可以使用 `port` 选项指定端口号。
¥You can specify the port number with the `port` option.
```ts
serve({
fetch: app.fetch,
port: 8787,
})
```
## 访问原始 Node.js API
¥Access the raw Node.js APIs
你可以从 `c.env.incoming` 和 `c.env.outgoing` 访问 Node.js API。
¥You can access the Node.js APIs from `c.env.incoming` and `c.env.outgoing`.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { serve, type HttpBindings } from '@hono/node-server'
// or `Http2Bindings` if you use HTTP2
type Bindings = HttpBindings & {
/* ... */
}
const app = new Hono<{ Bindings: Bindings }>()
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.json({
remoteAddress: c.env.incoming.socket.remoteAddress,
})
})
serve(app)
```
## 提供静态文件
¥Serve static files
你可以使用 `serveStatic` 从本地文件系统提供静态文件。例如,假设目录结构如下:
¥You can use `serveStatic` to serve static files from the local file system. For example, suppose the directory structure is as follows:
```sh
./
├── favicon.ico
├── index.ts
└── static
├── hello.txt
└── image.png
```
如果访问路径 `/static/*` 并返回 `./static` 下的文件,你可以编写以下内容:
¥If access to the path `/static/*` comes in and returns a file under `./static`, you can write the following:
```ts
import { serveStatic } from '@hono/node-server/serve-static'
app.use('/static/*', serveStatic({ root: './' }))
```
使用 `path` 选项在目录根中提供 `favicon.ico`:
¥Use the `path` option to serve `favicon.ico` in the directory root:
```ts
app.use('/favicon.ico', serveStatic({ path: './favicon.ico' }))
```
如果访问路径 `/hello.txt` 或 `/image.png` 并返回名为 `./static/hello.txt` 或 `./static/image.png` 的文件,你可以使用以下内容:
¥If access comes to the path `/hello.txt` or `/image.png` and returns a file named `./static/hello.txt` or `./static/image.png`, you can use the following:
```ts
app.use('*', serveStatic({ root: './static' }))
```
### `rewriteRequestPath`
如果你想要将 `http://localhost:3000/static/*` 映射到 `./statics`,你可以使用 `rewriteRequestPath` 选项:
¥If you want to map `http://localhost:3000/static/*` to `./statics`, you can use the `rewriteRequestPath` option:
```ts
app.get(
'/static/*',
serveStatic({
root: './',
rewriteRequestPath: (path) =>
path.replace(/^\/static/, '/statics'),
})
)
```
## http2
你可以在 [Node.js http2 服务器](https://nodejs.cn/api/http2.html) 上运行 hono。
¥You can run hono on a [Node.js http2 Server](https://nodejs.cn/api/http2.html).
### 未加密 http2
¥unencrypted http2
```ts
import { createServer } from 'node:http2'
const server = serve({
fetch: app.fetch,
createServer,
})
```
### 加密 http2
¥encrypted http2
```ts
import { createSecureServer } from 'node:http2'
import { readFileSync } from 'node:fs'
const server = serve({
fetch: app.fetch,
createServer: createSecureServer,
serverOptions: {
key: readFileSync('localhost-privkey.pem'),
cert: readFileSync('localhost-cert.pem'),
},
})
```
## 构建和部署
¥Building & Deployment
完成以下步骤以构建一个简单的 Hono 应用。具有前端框架的应用可能需要使用 [Hono 的 Vite 插件](https://github.com/honojs/vite-plugins)。
¥Complete the following steps to build a simple Hono app. Apps with a front-end framework may need to use [Hono's Vite plugins](https://github.com/honojs/vite-plugins).
1. 将 `"outDir": "./dist"` 添加到 `tsconfig.json` 的 `compilerOptions` 部分。
¥Add `"outDir": "./dist"` to the `compilerOptions` section `tsconfig.json`.
2. 将 `"exclude": ["node_modules"]` 添加到 `tsconfig.json`。
¥Add `"exclude": ["node_modules"]` to `tsconfig.json`.
3. 将 `"build": "tsc"` 添加到 `package.json` 的 `script` 部分。
¥Add `"build": "tsc"` to `script` section of `package.json`.
4. 运行 `npm install typescript --save-dev`。
¥Run `npm install typescript --save-dev`.
5. 将 `"type": "module"` 添加到 `package.json`。
¥Add `"type": "module"` to `package.json`.
6. 运行 `npm run build`!
¥Run `npm run build`!
### Dockerfile
以下是 Dockerfile 的示例。你必须完成上述步骤 1-5,此构建和部署过程才能工作。
¥Here is an example of a Dockerfile. You must complete steps 1-5 above before this build and deployment process will work.
```Dockerfile
FROM node:20-alpine AS base
FROM base AS builder
RUN apk add --no-cache gcompat
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*json tsconfig.json src ./
RUN npm ci && \
npm run build && \
npm prune --production
FROM base AS runner
WORKDIR /app
RUN addgroup --system --gid 1001 nodejs
RUN adduser --system --uid 1001 hono
COPY --from=builder --chown=hono:nodejs /app/node_modules /app/node_modules
COPY --from=builder --chown=hono:nodejs /app/dist /app/dist
COPY --from=builder --chown=hono:nodejs /app/package.json /app/package.json
USER hono
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "/app/dist/index.js"]
```
# 服务工作线程
¥Service Worker
[服务工作线程](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/Service_Worker_API) 是一个在浏览器后台运行的脚本,用于处理缓存和推送通知等任务。使用 Service Worker 适配器,你可以在浏览器中运行使用 Hono 作为 [FetchEvent](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/FetchEvent) 处理程序制作的应用。
¥[Service Worker](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/Service_Worker_API) is a script that runs in the background of the browser to handle tasks like caching and push notifications. Using a Service Worker adapter, you can run applications made with Hono as [FetchEvent](https://web.nodejs.cn/en-US/docs/Web/API/FetchEvent) handler within the browser.
此页面显示了使用 [Vite](https://vitejs.dev/) 创建项目的示例。
¥This page shows an example of creating a project using [Vite](https://vitejs.dev/).
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
首先,创建并移动到你的项目目录:
¥First, create and move to your project directory:
```sh
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
```
为项目创建必要的文件。使用以下内容创建 `package.json` 文件:
¥Create the necessary files for the project. Make a `package.json` file with the following:
```json
{
"name": "my-app",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"dev": "vite dev"
},
"type": "module"
}
```
类似地,创建一个包含以下内容的 `tsconfig.json` 文件:
¥Similarly, create a `tsconfig.json` file with the following:
```json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2020",
"module": "ESNext",
"lib": ["ES2020", "DOM", "WebWorker"],
"moduleResolution": "bundler"
},
"include": ["./"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}
```
接下来,安装必要的模块。
¥Next, install the necessary modules.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i hono
npm i -D vite
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add hono
yarn add -D vite
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add hono
pnpm add -D vite
```
```sh [bun]
bun add hono
bun add -D vite
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
编辑 `index.html`:
¥Edit `index.html`:
```html
Hello World by Service Worker
```
`main.ts` 是一个用于注册 Service Worker 的脚本:
¥`main.ts` is a script to register the Service Worker:
```ts
function register() {
navigator.serviceWorker
.register('/sw.ts', { scope: '/sw', type: 'module' })
.then(
function (_registration) {
console.log('Register Service Worker: Success')
},
function (_error) {
console.log('Register Service Worker: Error')
}
)
}
function start() {
navigator.serviceWorker
.getRegistrations()
.then(function (registrations) {
for (const registration of registrations) {
console.log('Unregister Service Worker')
registration.unregister()
}
register()
})
}
start()
```
在 `sw.ts` 中,使用 Hono 创建一个应用,并使用 Service Worker 适配器的 `handle` 函数将其注册到 `fetch` 事件。这允许 Hono 应用拦截对 `/sw` 的访问。
¥In `sw.ts`, create an application using Hono and register it to the `fetch` event with the Service Worker adapter’s `handle` function. This allows the Hono application to intercept access to `/sw`.
```ts
// To support types
// https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/issues/14877
declare const self: ServiceWorkerGlobalScope
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/service-worker'
const app = new Hono().basePath('/sw')
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello World'))
self.addEventListener('fetch', handle(app))
```
## 3. 运行
¥ Run
启动开发服务器。
¥Start the development server.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm run dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
默认情况下,开发服务器将在端口 `5173` 上运行。在你的浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:5173/` 以完成 Service Worker 注册。然后,访问 `/sw` 以查看来自 Hono 应用的响应。
¥By default, the development server will run on port `5173`. Access `http://localhost:5173/` in your browser to complete the Service Worker registration. Then, access `/sw` to see the response from the Hono application.
# Supabase 边缘函数
¥Supabase Edge Functions
[Supabase](https://supabase.com/) 是 Firebase 的开源替代品,提供一套类似于 Firebase 功能的工具,包括数据库、身份验证、存储以及现在的无服务器功能。
¥[Supabase](https://supabase.com/) is an open-source alternative to Firebase, offering a suite of tools similar to Firebase's capabilities, including database, authentication, storage, and now, serverless functions.
Supabase Edge Functions 是服务器端 TypeScript 函数,它们分布在全球各地,更靠近你的用户运行以提高性能。这些函数是使用 [Deno](https://deno.com/) 开发的,它带来了许多好处,包括改进的安全性和现代 JavaScript/TypeScript 运行时。
¥Supabase Edge Functions are server-side TypeScript functions that are distributed globally, running closer to your users for improved performance. These functions are developed using [Deno](https://deno.com/), which brings several benefits, including improved security and a modern JavaScript/TypeScript runtime.
以下是开始使用 Supabase Edge Functions 的方法:
¥Here's how you can get started with Supabase Edge Functions:
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
### 先决条件
¥Prerequisites
在开始之前,请确保你已安装 Supabase CLI。如果你还没有安装,请按照 [官方文档](https://supabase.com/docs/guides/cli/getting-started) 中的说明进行操作。
¥Before you begin, make sure you have the Supabase CLI installed. If you haven't installed it yet, follow the instructions in the [official documentation](https://supabase.com/docs/guides/cli/getting-started).
### 创建新的项目
¥Creating a New Project
1. 打开你的终端或命令提示符。
¥Open your terminal or command prompt.
2. 通过运行以下命令在本地计算机的目录中创建一个新的 Supabase 项目:
¥Create a new Supabase project in a directory on your local machine by running:
```bash
supabase init
```
此命令在当前目录中初始化一个新的 Supabase 项目。
¥This command initializes a new Supabase project in the current directory.
### 添加边缘函数
¥Adding an Edge Function
3. 在你的 Supabase 项目中,创建一个名为 `hello-world` 的新 Edge 函数:
¥Inside your Supabase project, create a new Edge Function named `hello-world`:
```bash
supabase functions new hello-world
```
此命令在你的项目中创建一个具有指定名称的新 Edge 函数。
¥This command creates a new Edge Function with the specified name in your project.
## 2. Hello World
通过修改文件 `supabase/functions/hello-world/index.ts` 来编辑 `hello-world` 函数:
¥Edit the `hello-world` function by modifying the file `supabase/functions/hello-world/index.ts`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'jsr:@hono/hono'
// change this to your function name
const functionName = 'hello-world'
const app = new Hono().basePath(`/${functionName}`)
app.get('/hello', (c) => c.text('Hello from hono-server!'))
Deno.serve(app.fetch)
```
## 3. 运行
¥ Run
要在本地运行该函数,请使用以下命令:
¥To run the function locally, use the following command:
1. 使用以下命令提供该功能:
¥Use the following command to serve the function:
```bash
supabase start # start the supabase stack
supabase functions serve --no-verify-jwt # start the Functions watcher
```
`--no-verify-jwt` 标志允许你在本地开发期间绕过 JWT 验证。
¥The `--no-verify-jwt` flag allows you to bypass JWT verification during local development.
2. 使用 cURL 或 Postman 向 `http://127.0.0.1:54321/functions/v1/hello-world/hello` 发出 GET 请求:
¥Make a GET request using cURL or Postman to `http://127.0.0.1:54321/functions/v1/hello-world/hello`:
```bash
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:54321/functions/v1/hello-world/hello'
```
此请求应返回文本 "来自 hono-server 的问候!"。
¥This request should return the text "Hello from hono-server!".
## 4. 部署
¥ Deploy
你可以使用单个命令在 Supabase 中部署所有 Edge 函数:
¥You can deploy all of your Edge Functions in Supabase with a single command:
```bash
supabase functions deploy
```
或者,你可以通过在部署命令中指定函数名称来部署单个边缘函数:
¥Alternatively, you can deploy individual Edge Functions by specifying the name of the function in the deploy command:
```bash
supabase functions deploy hello-world
```
有关更多部署方法,请访问 Supabase 的 [部署到生产环境](https://supabase.com/docs/guides/functions/deploy) 文档。
¥For more deployment methods, visit the Supabase documentation on [Deploying to Production](https://supabase.com/docs/guides/functions/deploy).
# Vercel
Vercel 是面向前端开发者的平台,提供创新者在灵感迸发时所需的速度和可靠性。本节介绍在 Vercel 上运行的 Next.js。
¥Vercel is the platform for frontend developers, providing the speed and reliability innovators need to create at the moment of inspiration. This section introduces Next.js running on Vercel.
Next.js 是一个灵活的 React 框架,可为你提供构建块以创建快速的 Web 应用。
¥Next.js is a flexible React framework that gives you building blocks to create fast web applications.
在 Next.js 中,[边缘函数](https://vercel.com/docs/concepts/functions/edge-functions) 允许你在 Edge Runtime 上创建动态 API,例如 Vercel。使用 Hono,你可以用与其他运行时相同的语法编写 API 并使用许多中间件。
¥In Next.js, [Edge Functions](https://vercel.com/docs/concepts/functions/edge-functions) allows you to create dynamic APIs on Edge Runtime such as Vercel.
With Hono, you can write APIs with the same syntax as other runtimes and use many middleware.
## 1. 设置
¥ Setup
Next.js 的启动器可用。使用 "create-hono" 命令启动你的项目。为此示例选择 `nextjs` 模板。
¥A starter for Next.js is available.
Start your project with "create-hono" command.
Select `nextjs` template for this example.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn create hono my-app
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm create hono my-app
```
```sh [bun]
bun create hono@latest my-app
```
```sh [deno]
deno init --npm hono my-app
```
:::
移入 `my-app` 并安装依赖。
¥Move into `my-app` and install the dependencies.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
cd my-app
npm i
```
```sh [yarn]
cd my-app
yarn
```
```sh [pnpm]
cd my-app
pnpm i
```
```sh [bun]
cd my-app
bun i
```
:::
## 2. Hello World
如果你使用 App Router,请编辑 `app/api/[[...route]]/route.ts`。请参阅 [支持的 HTTP 方法](https://next.nodejs.cn/docs/app/building-your-application/routing/route-handlers#supported-http-methods) 部分了解更多选项。
¥If you use the App Router, Edit `app/api/[[...route]]/route.ts`. Refer to the [Supported HTTP Methods](https://next.nodejs.cn/docs/app/building-your-application/routing/route-handlers#supported-http-methods) section for more options.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/vercel'
export const runtime = 'edge'
const app = new Hono().basePath('/api')
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: 'Hello Next.js!',
})
})
export const GET = handle(app)
export const POST = handle(app)
```
如果你使用 Pages Router,请编辑 `pages/api/[[...route]].ts`。
¥If you use the Pages Router, Edit `pages/api/[[...route]].ts`.
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/vercel'
import type { PageConfig } from 'next'
export const config: PageConfig = {
runtime: 'edge',
}
const app = new Hono().basePath('/api')
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: 'Hello Next.js!',
})
})
export default handle(app)
```
## 3. 运行
¥ Run
在本地运行开发服务器。然后,在你的 Web 浏览器中访问 `http://localhost:3000`。
¥Run the development server locally. Then, access `http://localhost:3000` in your Web browser.
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm run dev
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn dev
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm dev
```
```sh [bun]
bun run dev
```
:::
现在,`/api/hello` 只返回 JSON,但如果你构建 React UI,则可以使用 Hono 创建一个全栈应用。
¥Now, `/api/hello` just returns JSON, but if you build React UIs, you can create a full-stack application with Hono.
## 4. 部署
¥ Deploy
如果你有 Vercel 账户,可以通过链接 Git 仓库进行部署。
¥If you have a Vercel account, you can deploy by linking the Git repository.
## Node.js
你还可以在 Node.js 运行时上运行 Next.js 上的 Hono。
¥You can also run Hono on Next.js running on the Node.js runtime.
### 应用路由
¥App Router
对于 App Router,你只需在路由处理程序中将运行时设置为 `nodejs`:
¥For the App Router, you can simply set the runtime to `nodejs` in your route handler:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/vercel'
export const runtime = 'nodejs'
const app = new Hono().basePath('/api')
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: 'Hello from Hono!',
})
})
export const GET = handle(app)
export const POST = handle(app)
```
### 页面路由
¥Pages Router
对于 Pages Router,你需要先安装 Node.js 适配器:
¥For the Pages Router, you'll need to install the Node.js adapter first:
::: code-group
```sh [npm]
npm i @hono/node-server
```
```sh [yarn]
yarn add @hono/node-server
```
```sh [pnpm]
pnpm add @hono/node-server
```
```sh [bun]
bun add @hono/node-server
```
:::
然后,你可以使用从 `@hono/node-server/vercel` 导入的 `handle` 函数:
¥Then, you can utilize the `handle` function imported from `@hono/node-server/vercel`:
```ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from '@hono/node-server/vercel'
import type { PageConfig } from 'next'
export const config: PageConfig = {
api: {
bodyParser: false,
},
}
const app = new Hono().basePath('/api')
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: 'Hello from Hono!',
})
})
export default handle(app)
```
为了使其与 Pages Router 配合使用,重要的是通过在项目仪表板或 `.env` 文件中设置环境变量来禁用 Vercel Node.js 助手:
¥In order for this to work with the Pages Router, it's important to disable Vercel Node.js helpers by setting up an environment variable in your project dashboard or in your `.env` file:
```text
NODEJS_HELPERS=0
```
# 上下文
¥Context
要处理请求和响应,可以使用 `Context` 对象。
¥To handle Request and Response, you can use `Context` object.
## req
`req` 是 HonoRequest 的实例。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 [HonoRequest](/docs/api/request)。
¥`req` is the instance of HonoRequest. For more details, see [HonoRequest](/docs/api/request).
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
const userAgent = c.req.header('User-Agent')
// ...
// ---cut-start---
return c.text(`Hello, ${userAgent}`)
// ---cut-end---
})
```
## body()
返回 HTTP 响应。
¥Return the HTTP response.
你可以使用 `c.header()` 设置标头,并使用 `c.status` 设置 HTTP 状态代码。这也可以在 `c.text()`、`c.json()` 等中设置。
¥You can set headers with `c.header()` and set HTTP status code with `c.status`.
This can also be set in `c.text()`, `c.json()` and so on.
::: info 信息
注意:返回文本或 HTML 时,建议使用 `c.text()` 或 `c.html()`。
¥**Note**: When returning Text or HTML, it is recommended to use `c.text()` or `c.html()`.
:::
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/welcome', (c) => {
// Set headers
c.header('X-Message', 'Hello!')
c.header('Content-Type', 'text/plain')
// Set HTTP status code
c.status(201)
// Return the response body
return c.body('Thank you for coming')
})
```
你还可以编写以下内容。
¥You can also write the following.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/welcome', (c) => {
return c.body('Thank you for coming', 201, {
'X-Message': 'Hello!',
'Content-Type': 'text/plain',
})
})
```
响应与下面相同。
¥The Response is the same as below.
```ts twoslash
new Response('Thank you for coming', {
status: 201,
headers: {
'X-Message': 'Hello!',
'Content-Type': 'text/plain',
},
})
```
## text()
将文本渲染为 `Content-Type:text/plain`。
¥Render text as `Content-Type:text/plain`.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/say', (c) => {
return c.text('Hello!')
})
```
## json()
将 JSON 渲染为 `Content-Type:application/json`。
¥Render JSON as `Content-Type:application/json`.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/api', (c) => {
return c.json({ message: 'Hello!' })
})
```
## html()
将 HTML 渲染为 `Content-Type:text/html`。
¥Render HTML as `Content-Type:text/html`.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html('
Hello! Hono!
')
})
```
## notFound()
返回 `Not Found` 响应。
¥Return the `Not Found` Response.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/notfound', (c) => {
return c.notFound()
})
```
## redirect()
重定向,默认状态代码为 `302`。
¥Redirect, default status code is `302`.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/redirect', (c) => {
return c.redirect('/')
})
app.get('/redirect-permanently', (c) => {
return c.redirect('/', 301)
})
```
## res
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
// Response object
app.use('/', async (c, next) => {
await next()
c.res.headers.append('X-Debug', 'Debug message')
})
```
## set() / get()
获取和设置任意键值对,具有当前请求的生命周期。这允许在中间件之间或从中间件到路由处理程序传递特定值。
¥Get and set arbitrary key-value pairs, with a lifetime of the current request. This allows passing specific values between middleware or from middleware to route handlers.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono<{ Variables: { message: string } }>()
// ---cut---
app.use(async (c, next) => {
c.set('message', 'Hono is cool!!')
await next()
})
app.get('/', (c) => {
const message = c.get('message')
return c.text(`The message is "${message}"`)
})
```
将 `Variables` 作为泛型传递给 `Hono` 的构造函数,使其类型安全。
¥Pass the `Variables` as Generics to the constructor of `Hono` to make it type-safe.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
// ---cut---
type Variables = {
message: string
}
const app = new Hono<{ Variables: Variables }>()
```
`c.set`/`c.get` 的值仅在同一请求中保留。它们不能在不同的请求之间共享或持久化。
¥The value of `c.set` / `c.get` are retained only within the same request. They cannot be shared or persisted across different requests.
## var
你还可以使用 `c.var` 访问变量的值。
¥You can also access the value of a variable with `c.var`.
```ts twoslash
import type { Context } from 'hono'
declare const c: Context
// ---cut---
const result = c.var.client.oneMethod()
```
如果你想要创建提供自定义方法的中间件,请像下面这样写:
¥If you want to create the middleware which provides a custom method,
write like the following:
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { createMiddleware } from 'hono/factory'
// ---cut---
type Env = {
Variables: {
echo: (str: string) => string
}
}
const app = new Hono()
const echoMiddleware = createMiddleware(async (c, next) => {
c.set('echo', (str) => str)
await next()
})
app.get('/echo', echoMiddleware, (c) => {
return c.text(c.var.echo('Hello!'))
})
```
如果要在多个处理程序中使用中间件,可以使用 `app.use()`。然后,你必须将 `Env` 作为泛型传递给 `Hono` 的构造函数以使其类型安全。
¥If you want to use the middleware in multiple handlers, you can use `app.use()`.
Then, you have to pass the `Env` as Generics to the constructor of `Hono` to make it type-safe.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import type { MiddlewareHandler } from 'hono/types'
declare const echoMiddleware: MiddlewareHandler
type Env = {
Variables: {
echo: (str: string) => string
}
}
// ---cut---
const app = new Hono()
app.use(echoMiddleware)
app.get('/echo', (c) => {
return c.text(c.var.echo('Hello!'))
})
```
## render() / setRenderer()
你可以在自定义中间件中使用 `c.setRenderer()` 设置布局。
¥You can set a layout using `c.setRenderer()` within a custom middleware.
```tsx twoslash
/** @jsx jsx */
/** @jsxImportSource hono/jsx */
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.use(async (c, next) => {
c.setRenderer((content) => {
return c.html(
{content}
)
})
await next()
})
```
然后,你可以利用 `c.render()` 在此布局中创建响应。
¥Then, you can utilize `c.render()` to create responses within this layout.
```ts twoslash
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
// ---cut---
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.render('Hello!')
})
```
其输出将是:
¥The output of which will be:
```html
Hello!
```
此外,此功能提供了自定义参数的灵活性。为了确保类型安全,类型可以定义为:
¥Additionally, this feature offers the flexibility to customize arguments.
To ensure type safety, types can be defined as:
```ts
declare module 'hono' {
interface ContextRenderer {
(
content: string | Promise,
head: { title: string }
): Response | Promise
}
}
```
以下是如何使用它的示例:
¥Here's an example of how you can use this:
```ts
app.use('/pages/*', async (c, next) => {
c.setRenderer((content, head) => {
return c.html(
{head.title}{head.title}