Appearance
Hono Stacks
Hono 使简单的事情变得简单,使困难的事情变得简单。它不仅适用于返回 JSON。但它也非常适合构建包括 REST API 服务器和客户端在内的全栈应用。
¥Hono makes easy things easy and hard things easy. It is suitable for not just only returning JSON. But it's also great for building the full-stack application including REST API servers and the client.
RPC
Hono 的 RPC 功能允许你在几乎不更改代码的情况下共享 API 规范。hc 生成的客户端将读取规范并访问类型安全的端点。
¥Hono's RPC feature allows you to share API specs with little change to your code. The client generated by hc will read the spec and access the endpoint type-safety.
以下库使之成为可能。
¥The following libraries make it possible.
我们可以将这些组件的集合称为 Hono Stack。现在让我们用它创建一个 API 服务器和一个客户端。
¥We can call the set of these components the Hono Stack. Now let's create an API server and a client with it.
编写 API
¥Writing API
首先,编写一个接收 GET 请求并返回 JSON 的端点。
¥First, write an endpoint that receives a GET request and returns JSON.
ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
return c.json({
message: `Hello!`,
})
})使用 Zod 进行验证
¥Validation with Zod
使用 Zod 验证以接收查询参数的值。
¥Validate with Zod to receive the value of the query parameter.
ts
import { zValidator } from '@hono/zod-validator'
import { z } from 'zod'
app.get(
'/hello',
zValidator(
'query',
z.object({
name: z.string(),
})
),
(c) => {
const { name } = c.req.valid('query')
return c.json({
message: `Hello! ${name}`,
})
}
)共享类型
¥Sharing the Types
要发出端点规范,请导出其类型。
¥To emit an endpoint specification, export its type.
警告
为了使 RPC 能够正确推断路由,所有包含的方法必须链接在一起,并且必须从声明的变量推断出端点或应用类型。有关更多信息,请参阅 RPC 的最佳实践。
¥For the RPC to infer routes correctly, all included methods must be chained, and the endpoint or app type must be inferred from a declared variable. For more, see Best Practices for RPC.
ts
const route = app.get(
'/hello',
zValidator(
'query',
z.object({
name: z.string(),
})
),
(c) => {
const { name } = c.req.valid('query')
return c.json({
message: `Hello! ${name}`,
})
}
)
export type AppType = typeof route客户端
¥Client
下一步。客户端实现。通过将 AppType 类型作为泛型传递给 hc 来创建客户端对象。然后,神奇的是,完成工作并建议端点路径和请求类型。
¥Next. The client-side implementation. Create a client object by passing the AppType type to hc as generics. Then, magically, completion works and the endpoint path and request type are suggested.
ts
import { AppType } from './server'
import { hc } from 'hono/client'
const client = hc<AppType>('/api')
const res = await client.hello.$get({
query: {
name: 'Hono',
},
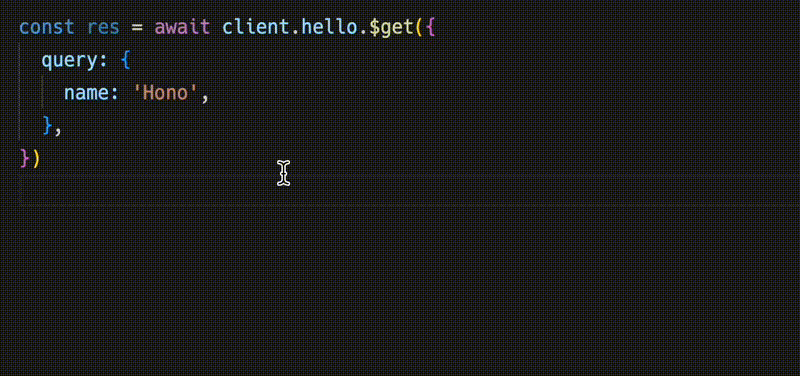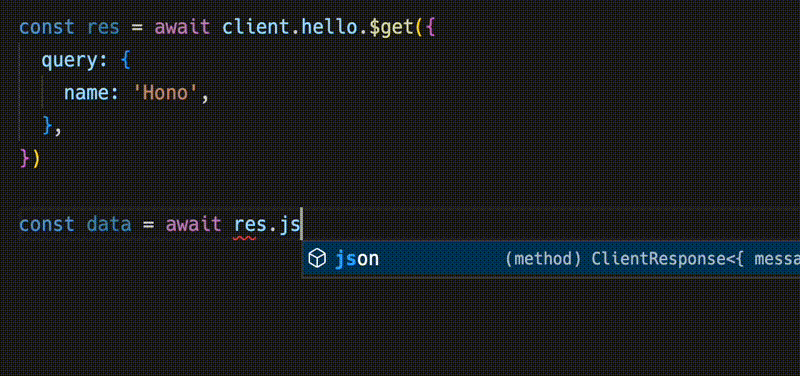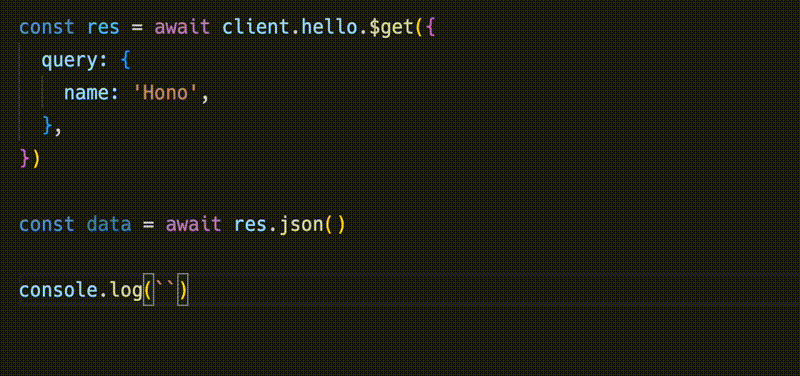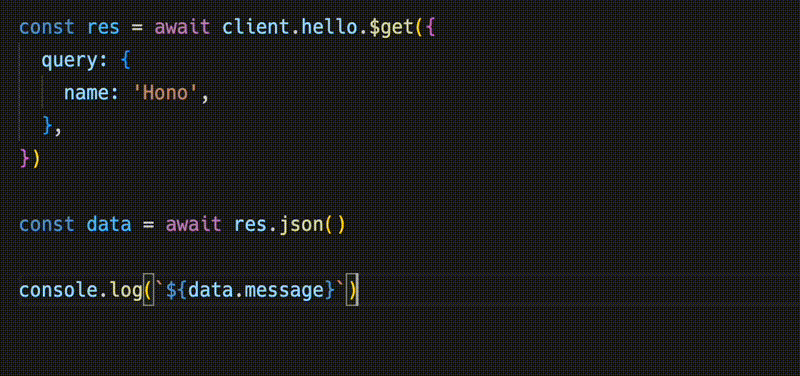
})Response 与 fetch API 兼容,但可以用 json() 检索的数据具有类型。
¥The Response is compatible with the fetch API, but the data that can be retrieved with json() has a type.
ts
const data = await res.json()
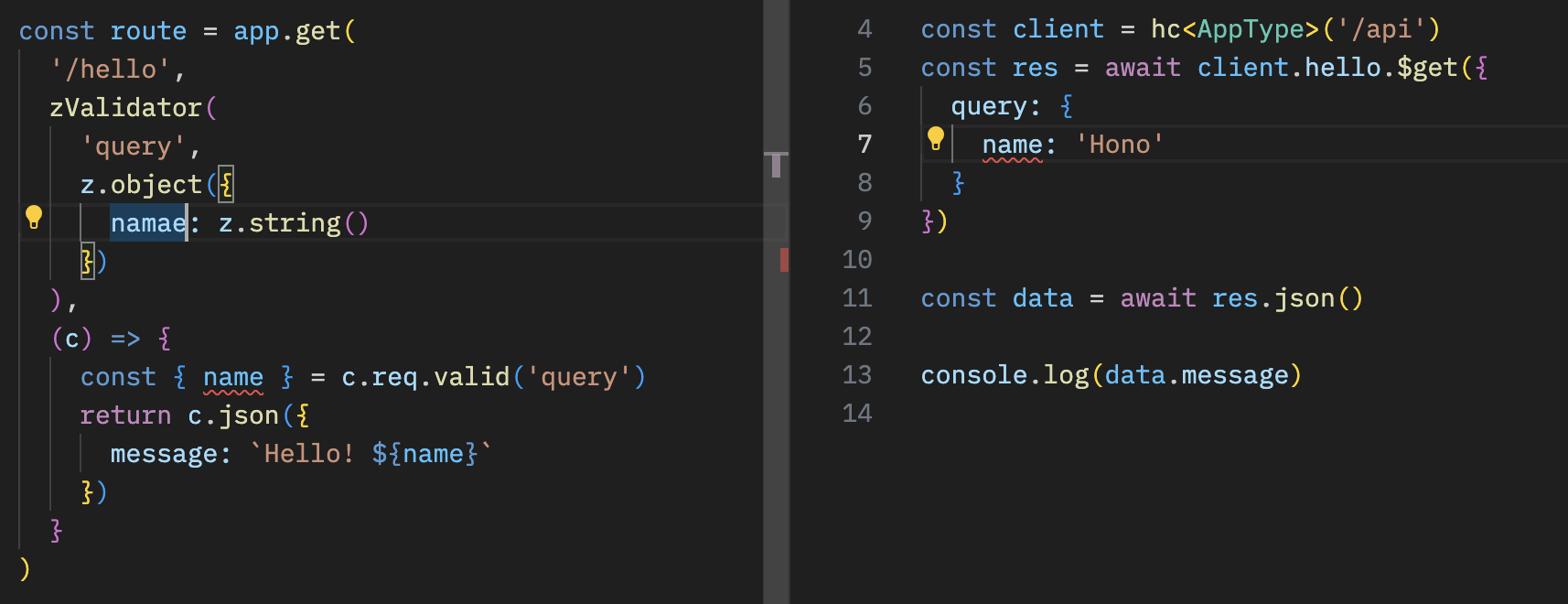
console.log(`${data.message}`)共享 API 规范意味着你可以了解服务器端的变化。
¥Sharing API specifications means that you can be aware of server-side changes.
使用 React
¥With React
你可以使用 React 在 Cloudflare Pages 上创建应用。
¥You can create applications on Cloudflare Pages using React.
API 服务器。
¥The API server.
ts
// functions/api/[[route]].ts
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { handle } from 'hono/cloudflare-pages'
import { z } from 'zod'
import { zValidator } from '@hono/zod-validator'
const app = new Hono()
const schema = z.object({
id: z.string(),
title: z.string(),
})
type Todo = z.infer<typeof schema>
const todos: Todo[] = []
const route = app
.post('/todo', zValidator('form', schema), (c) => {
const todo = c.req.valid('form')
todos.push(todo)
return c.json({
message: 'created!',
})
})
.get((c) => {
return c.json({
todos,
})
})
export type AppType = typeof route
export const onRequest = handle(app, '/api')带有 React 和 React Query 的客户端。
¥The client with React and React Query.
tsx
// src/App.tsx
import {
useQuery,
useMutation,
QueryClient,
QueryClientProvider,
} from '@tanstack/react-query'
import { AppType } from '../functions/api/[[route]]'
import { hc, InferResponseType, InferRequestType } from 'hono/client'
const queryClient = new QueryClient()
const client = hc<AppType>('/api')
export default function App() {
return (
<QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}>
<Todos />
</QueryClientProvider>
)
}
const Todos = () => {
const query = useQuery({
queryKey: ['todos'],
queryFn: async () => {
const res = await client.todo.$get()
return await res.json()
},
})
const $post = client.todo.$post
const mutation = useMutation<
InferResponseType<typeof $post>,
Error,
InferRequestType<typeof $post>['form']
>({
mutationFn: async (todo) => {
const res = await $post({
form: todo,
})
return await res.json()
},
onSuccess: async () => {
queryClient.invalidateQueries({ queryKey: ['todos'] })
},
onError: (error) => {
console.log(error)
},
})
return (
<div>
<button
onClick={() => {
mutation.mutate({
id: Date.now().toString(),
title: 'Write code',
})
}}
>
Add Todo
</button>
<ul>
{query.data?.todos.map((todo) => (
<li key={todo.id}>{todo.title}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
)
}